A Comparative In Vitro Evaluation of the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Tisochrysis lutea Extract and Fucoxanthin
- PMID: 34207952
- PMCID: PMC8230663
- DOI: 10.3390/md19060334
A Comparative In Vitro Evaluation of the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Tisochrysis lutea Extract and Fucoxanthin
Abstract
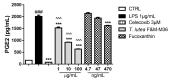
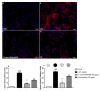
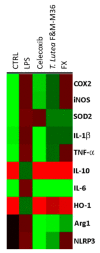
In this study, we compared the effects of a Tisochrysis lutea (T. lutea) F&M-M36 methanolic extract with those of fucoxanthin (FX) at equivalent concentration, on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. The T. lutea F&M-M36 methanolic extract contained 4.7 mg of FX and 6.22 mg of gallic acid equivalents of phenols per gram. HPLC analysis revealed the presence of simple phenolic acid derivatives. The T. lutea F&M-M36 extract exhibited a potent and concentration-dependent inhibitory activity against COX-2 dependent PGE2 production compared to FX alone. Compared to LPS, T. lutea F&M-M36 extract and FX reduced the expression of IL-6 and of Arg1 and enhanced that of IL-10 and of HO-1; T. lutea F&M-M36 extract also significantly abated the expression of NLRP3, enhanced mir-223 expression and reduced that of mir-146b, compared to LPS (p < 0.05). These findings indicate that T. lutea F&M-M36 methanolic extract has a peculiar anti-inflammatory activity against COX-2/PGE2 and NLRP3/mir-223 that might be attributable to the known anti-inflammatory effects of simple phenolic compounds found in the extract that may synergize with FX. Our data suggest that T. lutea F&M-M36 may serve as a source of anti-inflammatory compounds to be further evaluated in in vivo models of inflammation.
Keywords: RAW 264.7; Tisochrysis lutea; fucoxanthin; inflammation; microRNA; microalgae.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Bendif E., Probert I., Schroeder D.C., de Vargas C. On the description of Tisochrysis lutea gen. nov., sp. nov. and Isochrysis nuda sp. nov. in the Isochrysidales, and the transfer of Dicrateria to the Prymnesiales (Haptophyta) J. Appl. Phycol. 2013;25:1763–1776. doi: 10.1007/s10811-013-0037-0. - DOI
-
- Camacho-Rodríguez J., Cerón-García M.C., González-López C.V., López-Rosales L., Contreras-Gómez A., Molina-Grima E. Use of continuous culture to develop an economical medium for the mass production of Isochrysis galbana for aquaculture. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020;32:851–863. doi: 10.1007/s10811-019-02015-0. - DOI
-
- Custódio L., Soares F., Pereira H., Barreira L., Vizetto-Duarte C., Rodrigues M.J., Rauter A.P., Alberício F., Varela J. Fatty acid composition and biological activities of Isochrysis galbana T-ISO, Tetraselmis sp. and Scenedesmus sp.: Possible application in the pharmaceutical and functional food industries. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014;26:151–161. doi: 10.1007/s10811-013-0098-0. - DOI
-
- de los Reyes C., Ortega M.J., Rodríguez-Luna A., Talero E., Motilva V., Zubía E. Molecular characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of galactosylglycerides and galactosylceramides from the microalga Isochrysis galbana. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016;64:8783–8794. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b03931. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

