Characterization and Quantification of Selenoprotein P: Challenges to Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 34208081
- PMCID: PMC8230778
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22126283
Characterization and Quantification of Selenoprotein P: Challenges to Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
Selenoprotein P (SELENOP) is an emerging marker of the nutritional status of selenium and of various diseases, however, its chemical characteristics still need to be investigated and methods for its accurate quantitation improved. SELENOP is unique among selenoproteins, as it contains multiple genetically encoded SeCys residues, whereas all the other characterized selenoproteins contain just one. SELENOP occurs in the form of multiple isoforms, truncated species and post-translationally modified variants which are relatively poorly characterized. The accurate quantification of SELENOP is contingent on the availability of specific primary standards and reference methods. Before recombinant SELENOP becomes available to be used as a primary standard, careful investigation of the characteristics of the SELENOP measured by electrospray MS and strict control of the recoveries at the various steps of the analytical procedures are strongly recommended. This review critically discusses the state-of-the-art of analytical approaches to the characterization and quantification of SELENOP. While immunoassays remain the standard for the determination of human and animal health status, because of their speed and simplicity, mass spectrometry techniques offer many attractive and complementary features that are highlighted and critically evaluated.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer; mass spectrometry; metrology; selenium; selenocysteine; selenoprotein P.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
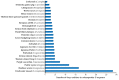
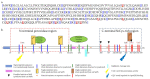

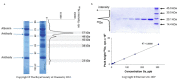
References
-
- Hatfield D.L., Schweizer U., Tsuji P.A., Gladyshev V.N., editors. Selenium: Its Molecular Biology and Role in Human Health. Springer Science & Business Media; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

