Ion Channel Gene Mutations Causing Skeletal Muscle Disorders: Pathomechanisms and Opportunities for Therapy
- PMID: 34208776
- PMCID: PMC8234207
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10061521
Ion Channel Gene Mutations Causing Skeletal Muscle Disorders: Pathomechanisms and Opportunities for Therapy
Abstract
Skeletal muscle ion channelopathies (SMICs) are a large heterogeneous group of rare genetic disorders caused by mutations in genes encoding ion channel subunits in the skeletal muscle mainly characterized by myotonia or periodic paralysis, potentially resulting in long-term disabilities. However, with the development of new molecular technologies, new genes and new phenotypes, including progressive myopathies, have been recently discovered, markedly increasing the complexity in the field. In this regard, new advances in SMICs show a less conventional role of ion channels in muscle cell division, proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Hence, SMICs represent an expanding and exciting field. Here, we review current knowledge of SMICs, with a description of their clinical phenotypes, cellular and molecular pathomechanisms, and available treatments.
Keywords: CACNA1S; CLCN1; KCNJ2; SCN4A; ion channels; myopathies; myotonia; periodic paralysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no disclosure relevant to the manuscript.
Figures
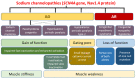
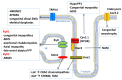
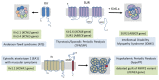
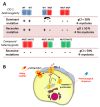
References
-
- Stunnenberg B.C., Raaphorst J., Deenen J.C., Links T.P., Wilde A.A., Verbove D.J., Kamsteeg E.J., van den Wijngaard A., Faber C.G., van der Wilt G.J., et al. Prevalence and mutation spectrum of skeletal muscle channelopathies in the Netherlands. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2018;28:402–407. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2018.03.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maggi L., Brugnoni R., Canioni E., Tonin P., Saletti V., Patrizia S., Cotti Piccinelli S., Colleoni L., Ferrigno P., Antonella P., et al. Clinical and Molecular Spectrum of Myotonia and Periodic Paralyses Associated With Mutations in SCN4A in a Large Cohort of Italian Patients. Front. Neurol. 2020;11:646. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00646. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

