Metastatic Risk Factors Associated with Class 1A Uveal Melanoma Patients
- PMID: 34209210
- PMCID: PMC8269154
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13133292
Metastatic Risk Factors Associated with Class 1A Uveal Melanoma Patients
Abstract
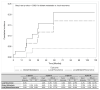
In uveal melanoma (UM), gene expression profiling (GEP) is commonly used to classify metastatic risk into three groups (Class 1A, 1B, and 2). Class 1A patients have a lower metastatic risk of 2% at 5 years compared to other groups. We aimed to describe clinical features associated with the development of metastasis in this low-risk group. This single-center IRB-approved retrospective case series review included all UM patients between February 2006 and March 2019 with an archived or fresh specimen classified as Class 1A. Cox regression and receiver operating characteristics analyses were used to identify factors associated with metastasis development and OS. Among 73 UM patients with Class 1A, the 5-year cumulative incidence of local recurrence and distant metastasis was 4.2% and 17.0%, respectively. Stage III disease (HR 20.7; 95% confidence interval (95% CI) 1.4-300.6; p = 0.0264) was found to be independently associated with metastatic recurrence, while primary therapy was associated with OS (enucleation vs. brachytherapy, HR 13.5; 95% CI 1.3-147.6; p = 0.0348). Combined clinical decision-making utilizing factors such as GEP class, American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage, and COMS size could have a significant clinical impact by improving risk stratification and adapting follow-up intervals in UM Class 1A patients.
Keywords: Class 1A; GEP; metastasis; risk factors; uveal melanoma.
Conflict of interest statement
S.P.P. reports honoraria for Scientific Advisory Board participation from Castle Biosciences (cutaneous melanoma). All other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Onken M.D., Worley L.A., Char D.H., Augsburger J.J., Correa Z.M., Nudleman E., Aaberg T.M., Jr., Altaweel M.M., Bardenstein D.S., Finger P.T., et al. Collaborative Ocular Oncology Group report number 1: Prospective validation of a multi-gene prognostic assay in uveal melanoma. Ophthalmology. 2012;119:1596–1603. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.02.017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

