Norovirus VPg Binds RNA through a Conserved N-Terminal K/R Basic Patch
- PMID: 34209211
- PMCID: PMC8310136
- DOI: 10.3390/v13071282
Norovirus VPg Binds RNA through a Conserved N-Terminal K/R Basic Patch
Abstract
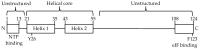
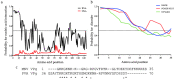
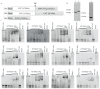
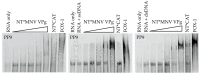
The viral protein genome-linked (VPg) of noroviruses is a multi-functional protein that participates in essential roles during the viral replication cycle. Predictive analyses indicate that murine norovirus (MNV) VPg contains a disordered N-terminal region with RNA binding potential. VPg proteins were expressed with an N-terminal spidroin fusion protein in insect cells and the interaction with RNA investigated by electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) against a series of RNA probes (pentaprobes) representing all possible five nucleotide combinations. MNV VPg and human norovirus (HuNV) VPg proteins were directly bound to RNA in a non-specific manner. To identify amino acids involved in binding to RNA, all basic (K/R) residues in the first 12 amino acids of MNV VPg were mutated to alanine. Removal of the K/R amino acids eliminated RNA binding and is consistent with a K/R basic patch RNA binding motif within the disordered N-terminal region of norovirus VPgs. Finally, we show that mutation of the K/R basic patch required for RNA binding eliminates the ability of MNV VPg to induce a G0/G1 cell cycle arrest.
Keywords: RNA binding; VPg; calicivirus; norovirus; spidroin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
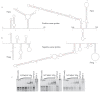


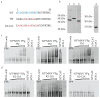
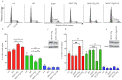
References
-
- Estes M.K., Ettayebi K., Tenge V.R., Murakami K., Karandikar U., Lin S.C., Ayyar B.V., Cortes-Penfield N.W., Haga K., Neill F.H., et al. Human Norovirus Cultivation in Nontransformed Stem Cell-Derived Human Intestinal Enteroid Cultures: Success and Challenges. Viruses. 2019;11:638. doi: 10.3390/v11070638. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

