Arbuscular Mycorrhizae Mitigate Aluminum Toxicity and Regulate Proline Metabolism in Plants Grown in Acidic Soil
- PMID: 34209315
- PMCID: PMC8304902
- DOI: 10.3390/jof7070531
Arbuscular Mycorrhizae Mitigate Aluminum Toxicity and Regulate Proline Metabolism in Plants Grown in Acidic Soil
Abstract
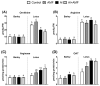
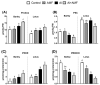
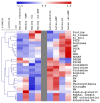
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) can promote plant growth and induce stress tolerance. Proline is reported to accumulate in mycorrhizal plants under stressful conditions, such as aluminum (Al) stress. However, the detailed changes induced in proline metabolism under AMF-plant symbiosis has not been studied. Accordingly, this work aimed to study how Al-stressed grass (barley) and legume (lotus) species respond to AMF inoculation at growth and biochemical levels. The associated changes in Al uptake and accumulation, the rate of photosynthesis, and the key enzymes and metabolites involved in proline biosynthesis and degradation pathways were studied. Soil contamination with Al induced Al accumulation in tissues of both species and, consequently, reduced plant growth and the rate of photosynthesis, while more tolerance was noticed in lotus. Inoculation with AMF significantly reduced Al accumulation and mitigated the negative impacts of Al on growth and photosynthesis in both species; however, these positive effects were more pronounced in barley plants. The mitigating action of AMF was associated with upregulation of proline biosynthesis through glutamate and ornithine pathways, more in lotus than in barley, and repression of its catabolism. The increased proline level in lotus was consistent with improved N metabolism (N level and nitrate reductase). Overall, this study suggests the role of AMF in mitigating Al stress, where regulation of proline metabolism is a worthy mechanism underlying this mitigating action.
Keywords: Rhizophagus irregularis; barley; lotus; nitrogen assimilation; photosynthesis; proline metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- de Sousa A., Saleh A.M., Habeeb T.H., Hassan Y.M., Zrieq R., Wadaan M.A.M., Hozzein W.N., Selim S., Matos M., AbdElgawad H. Silicon dioxide nanoparticles ameliorate the phytotoxic hazards of aluminum in maize grown on acidic soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019;693:133636. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133636. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dal Molin S.J., Ernani P.R., Gerber J.M. Soil acidification and nitrogen release following application of nitrogen fertilizers. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020;51:2551–2558. doi: 10.1080/00103624.2020.1845347. - DOI
-
- Pierre W.H., Webb J.R., Shrader W.D. Quantitative Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Development and Downward Movement of Soil Acidity in Relation to Level of Fertilization and Crop Removal in a Continuous Corn Cropping System1. Agron. J. 1971;63:291–297. doi: 10.2134/agronj1971.00021962006300020028x. - DOI
-
- Yamamoto Y. Aluminum toxicity in plant cells: Mechanisms of cell death and inhibition of cell elongation. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019;65:41–55. doi: 10.1080/00380768.2018.1553484. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

