A Combined Model and Data-Driven Approach for the Determination of Rotor Temperature in an Induction Machine
- PMID: 34209439
- PMCID: PMC8272216
- DOI: 10.3390/s21134512
A Combined Model and Data-Driven Approach for the Determination of Rotor Temperature in an Induction Machine
Abstract
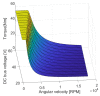
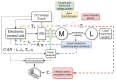
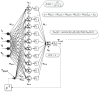
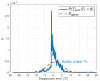
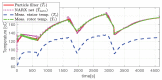
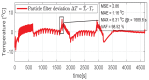
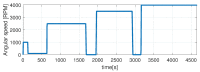
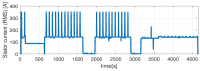
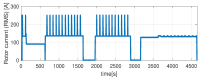
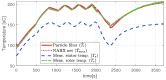
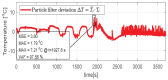
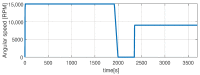
The need for protection of electrical machines comes as a demand of safety regulations in the automotive industry as well as a result of the general desire to obtain a robust and reliable electric powertrain. This paper introduces a hybrid method for estimating the temperature of the rotor of an Induction Machine (IM) based on a Nonlinear Autoregressive Network with Exogenous inputs (NARX) used as a prediction function within a particle filter. The temperature of the stator case is measured, and the information is used as an input to a NARX network and as a variable to a thermal process with first-order dynamics which serves as an observation function. Uncertainties of the NARX and thermal model are determined and used to correct the posterior estimate. Experimental data are used from a real IM test-bench and the results prove the applicability and good performance.
Keywords: AC machines; fault diagnosis; neural network applications; recursive estimation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Sharma V.K., Usman A., Rajpurohit B.S. Fault Diagnosis of BLDC Motor Drive using Vibration Spectrum Analysis: Part II; Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Power and Renewable Energy Conference; Karunagappally, India. 30 Octomber–1 November 2020; pp. 1–6. - DOI
-
- Usman A., Rajpurohit B.S. Time-Efficient Fault Diagnosis of a BLDC Motor Drive Deployed in Electric Vehicle Applications; Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Global Humanitarian Technology Conference (GHTC); Seattle, WA, USA. 29 Octomber–1 November 2020; pp. 1–5. - DOI
-
- Park H., Suh Y. Fault-Tolerant Control Strategy for Reduced Torque Ripple of Independent Twelve-phase BLDC Motor Drive System under Open-Circuit Faults; Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE); Detroit, MI, USA. 11–15 October 2020; pp. 3370–3375. - DOI
-
- Emadi A., Lee Y.J., Rajashekara K. Power electronics and motor drives in electric, hybrid electric, and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008;55:2237–2245. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2008.922768. - DOI
-
- Mocanu R., Onea A. Determination of stator temperature for thermal protection in a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine; Proceedings of the 2017 25th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation (MED); Valletta, Malta. 3–6 July 2017; pp. 1321–1325.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

