Macrophage Polarization States in the Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 34209703
- PMCID: PMC8268869
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22136995
Macrophage Polarization States in the Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
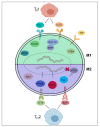
The M1/M2 macrophage paradigm plays a key role in tumor progression. M1 macrophages are historically regarded as anti-tumor, while M2-polarized macrophages, commonly deemed tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), are contributors to many pro-tumorigenic outcomes in cancer through angiogenic and lymphangiogenic regulation, immune suppression, hypoxia induction, tumor cell proliferation, and metastasis. The tumor microenvironment (TME) can influence macrophage recruitment and polarization, giving way to these pro-tumorigenic outcomes. Investigating TME-induced macrophage polarization is critical for further understanding of TAM-related pro-tumor outcomes and potential development of new therapeutic approaches. This review explores the current understanding of TME-induced macrophage polarization and the role of M2-polarized macrophages in promoting tumor progression.
Keywords: cytokine signaling; malignancy; metastasis; polarization; tumor microenvironment; tumor-associated macrophage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dijkgraaf E.M., Heusinkveld M., Tummers B., Vogelpoel L.T.C., Goedemans R., Jha V., Nortier J.W.R., Welters M.J.P., Kroep J.R., van der Burg S.H. Chemotherapy Alters Monocyte Differentiation to Favor Generation of Cancer-Supporting M2 Macrophages in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2013;73:2480–2492. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3542. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

