Characterization of Salmonella serotypes prevalent in asymptomatic people and patients
- PMID: 34210275
- PMCID: PMC8252320
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-021-06340-z
Characterization of Salmonella serotypes prevalent in asymptomatic people and patients
Abstract
Background: Infection with Salmonella enterica usually results in diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps, but some people become asymptomatic or chronic carrier as a source of infection for others. This study aimed to analyze the difference in serotype, antimicrobial resistance, and genetic profiles between Salmonella strains isolated from patients and those from asymptomatic people in Nantong city, China.
Methods: A total of 88 Salmonella strains were collected from patients and asymptomatic people from 2017 to 2018. Serotyping, antimicrobial susceptibility testing, and PFGE analysis were performed to analyze the characteristics of these strains.
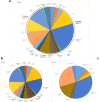
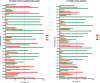
Results: Twenty serotypes belonging to 8 serogroups were identified in the 88 Salmonella strains. S. Typhimurium remained to be the predominant serotype in strains from both patients and asymptomatic people. Among the 27 strains from patients, S. Enteritidis and S. Rissen were shown as the other two major serotypes, while S. London, S. Derby, and S. Meleagridis were demonstrated as the other significant serotypes among the 61 strains from asymptomatic people. Antimicrobial resistance testing revealed that 84.1% of strains from both resources were multi-drug resistant. PFGE displayed a highly discriminative ability to differentiate strains belonging to S. Derby, S. Typhimurium, etc., but could not efficiently differentiate serotypes like S. Enteritidis.
Conclusions: This study's results demonstrated that S. Typhimurium could cause human infection in both symptomatic and asymptomatic state; S. London, S. Derby, and S. Meleagridis usually cause asymptomatic infection, while S. Enteritidis infection mainly results in human diseases. The high multi-drug resistance rate detected in the antimicrobial resistance and diverse PFGE profiles of these strains implied that the strains were isolated from different sources, and the increased surveillance of Salmonella from both patients and asymptomatic people should be taken to control the disease.
Keywords: Antimicrobial susceptibility; Asymptomatic infection; PFGE; Salmonella.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Harrois D, Breurec S, Seck A, Delaune A, Le Hello S, Pardos de la Gandara M, et al. Prevalence and characterization of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing clinical Salmonella enterica isolates in Dakar, Senegal, from 1999 to 2009. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20(2):109–116. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12339. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Majowicz SE, Musto J, Scallan E, Angulo FJ, Kirk M, O'Brien SJ, Jones TF, Fazil A, Hoekstra RM, International Collaboration on Enteric Disease 'Burden of Illness' Studies The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50(6):882–889. doi: 10.1086/650733. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

