Functional respiratory imaging assessment of budesonide/glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate and glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate metered dose inhalers in patients with COPD: the value of inhaled corticosteroids
- PMID: 34210340
- PMCID: PMC8247252
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-021-01772-2
Functional respiratory imaging assessment of budesonide/glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate and glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate metered dose inhalers in patients with COPD: the value of inhaled corticosteroids
Abstract
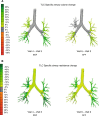
Background: For patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), greater improvements in lung function have been demonstrated for triple versus dual inhaled therapies in traditional spirometry studies. This study was the first to use functional respiratory imaging (FRI), known for increased sensitivity to airway changes versus spirometry, to assess the effect of the inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) component (budesonide) on lung function in patients with moderate-to-severe COPD and a blood eosinophil count > 150 cells/mm3.
Methods: Patients in this Phase IIIb (NCT03836677), randomized, double-blind, crossover study received twice-daily budesonide/glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate (BGF) 320/18/9.6 μg fixed-dose triple therapy and glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate (GFF) 18/9.6 μg fixed-dose dual therapy over 4 weeks, each delivered via a single metered dose Aerosphere inhaler. Primary endpoints were the improvements from baseline for each treatment in specific (i.e. corrected for lobar volume) image-based airway volume (siVaw) and resistance (siRaw) measured via FRI taken at total lung capacity (Day 29). Secondary outcomes included spirometry and body plethysmography. Adverse events were monitored throughout the study.
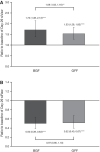
Results: A total of 23 patients were randomized and included in the intent-to-treat analysis (mean age 64.9 years, 78.3% males, 43.5% current smokers, mean predicted post-bronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 s [FEV1] 63.6%). BGF and GFF both statistically significantly increased siVaw from baseline at Day 29 (geometric mean ratio [GM], 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.72 [1.38, 2.13] and 1.53 [1.28, 1.83], respectively, both p < 0.0001), with a greater increase observed for BGF versus GFF (GM, 95% CI 1.09 [1.03, 1.16], p = 0.0061). Statistically significant reductions in siRaw were also observed with both BGF and GFF (GM, 95% CI 0.50 [0.39, 0.63] and 0.52 [0.40, 0.67], respectively, both p < 0.0001). Additionally, significant improvements from baseline in post-dose FEV1 were observed with BGF and GFF (mean 346 mL, p = 0.0003 and 273 mL, p = 0.0004, respectively). Safety findings were consistent with the known profiles of BGF and GFF.
Conclusions: As observed using FRI, triple therapy with BGF resulted in greater increases in airway volume, and reductions in airway resistance versus long-acting muscarinic antagonist/long-acting β2-agonist (LAMA/LABA) dual therapy with GFF, reflecting the ICS component's contribution in patients with moderate-to-severe COPD.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT03836677. Registered 11 February 2019, https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03836677.
Keywords: Budesonide; COPD; Formoterol fumarate; Functional respiratory imaging; Glycopyrrolate; Triple therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
MvdB reports research grants paid to his institution from AstraZeneca, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, and TEVA Pharma. JDB is the Chief Executive Officer and founder of FLUIDDA and holds shares in the company. CVH is an employee of FLUIDDA. WDB has no real or perceived conflicts of interest that relate to this manuscript. His department has received grants from AstraZeneca, Chiesi, and GlaxoSmithKline. RT, MJ, PD, and MA are employees of AstraZeneca and hold stock and/or stock options in the company.
Figures

References
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease report. 2020. https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/GOLD-2020-REPORT-ver1.0w.... Accessed March 02, 2021.
-
- Ferguson GT, Rabe KF, Martinez FJ, Fabbri LM, Wang C, Ichinose M, et al. Triple therapy with budesonide/glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate with co-suspension delivery technology versus dual therapies in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (KRONOS): a double-blind, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2018;6(10):747–758. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30327-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Israel S, Kumar A, DeAngelis K, Aurivillius M, Dorinsky P, Roche N, et al. Pulmonary deposition of budesonide/glycopyrronium/formoterol fumarate dihydrate metered dose inhaler formulated using co-suspension delivery technology in healthy male subjects. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020;153:105472. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105472. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Usmani O, Roche N, Abd Wahab E, Israel S, Jenkins M, Trivedi R, et al. A scintigraphy study of budesonide/glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate in patients with COPD. Chest. 2020;158(4):A2435–A2437. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.09.023. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

