Scalable and Robust Regression Methods for Phenome-Wide Association Analysis on Large-Scale Biobank Data
- PMID: 34211504
- PMCID: PMC8239389
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.682638
Scalable and Robust Regression Methods for Phenome-Wide Association Analysis on Large-Scale Biobank Data
Abstract
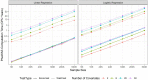
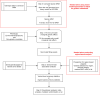
With the advances in genotyping technologies and electronic health records (EHRs), large biobanks have been great resources to identify novel genetic associations and gene-environment interactions on a genome-wide and even a phenome-wide scale. To date, several phenome-wide association studies (PheWAS) have been performed on biobank data, which provides comprehensive insights into many aspects of human genetics and biology. Although inspiring, PheWAS on large-scale biobank data encounters new challenges including computational burden, unbalanced phenotypic distribution, and genetic relationship. In this paper, we first discuss these new challenges and their potential impact on data analysis. Then, we summarize approaches that are scalable and robust in GWAS and PheWAS. This review can serve as a practical guide for geneticists, epidemiologists, and other medical researchers to identify genetic variations associated with health-related phenotypes in large-scale biobank data analysis. Meanwhile, it can also help statisticians to gain a comprehensive and up-to-date understanding of the current technical tool development.
Keywords: biobank data analysis; electronic health records-EHR; genetic relatedness; mixed model approaches; phenome-wide association studies; saddlepoint approximation; unbalanced phenotypic distribution.
Copyright © 2021 Bi and Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
INTEGRATING CLINICAL LABORATORY MEASURES AND ICD-9 CODE DIAGNOSES IN PHENOME-WIDE ASSOCIATION STUDIES.Pac Symp Biocomput. 2016;21:168-79. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2016. PMID: 26776183 Free PMC article.
-
A Fast and Accurate Method for Genome-wide Scale Phenome-wide G × E Analysis and Its Application to UK Biobank.Am J Hum Genet. 2019 Dec 5;105(6):1182-1192. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.10.008. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Am J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31735295 Free PMC article.
-
Robust meta-analysis of biobank-based genome-wide association studies with unbalanced binary phenotypes.Genet Epidemiol. 2019 Jul;43(5):462-476. doi: 10.1002/gepi.22197. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Genet Epidemiol. 2019. PMID: 30793809 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Electronic Health Records in Advancing Genomic Medicine.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2021 Aug 31;22:219-238. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-121120-125204. Epub 2021 May 26. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 34038146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenome-Wide Association Studies as a Tool to Advance Precision Medicine.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2016 Aug 31;17:353-73. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-090314-024956. Epub 2016 May 4. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27147087 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The integration of quantile regression with 3VmrMLM identifies more QTNs and QTN-by-environment interactions using SNP- and haplotype-based markers.Plant Commun. 2025 Mar 10;6(3):101196. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2024.101196. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Plant Commun. 2025. PMID: 39580620 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Current Status and Future Challenges of Biobank Data Analysis.Front Genet. 2022 Apr 14;13:882611. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.882611. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35495141 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Spatiotemporal and genetic regulation of A-to-I editing throughout human brain development.Cell Rep. 2022 Nov 1;41(5):111585. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111585. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36323256 Free PMC article.
-
SPAGRM: effectively controlling for sample relatedness in large-scale genome-wide association studies of longitudinal traits.Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 6;16(1):1413. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56669-1. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39915470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agresti A. (2003). Categorical Data Analysis. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
-
- Allaire J. J., François R., Ushey K., Vandenbrouck G., Geelnard M. (2018). RcppParallel: Parallel Programming Tools for ‘Rcpp’. R Package Version 4.4. 2.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources