Current treatment options for craniofacial hyperhidrosis
- PMID: 34211510
- PMCID: PMC8218019
- DOI: 10.1590/1677-5449.200152
Current treatment options for craniofacial hyperhidrosis
Abstract
Hyperhidrosis (HH) is characterized by sweating exceeding the amount necessary to meet the thermal regulation and physiological needs of the body. Approximately 9.41% of individuals with HH have craniofacial hyperhidrosis (FH). The present study aims to review the most current data in the literature regarding craniofacial hyperhidrosis, including pathophysiology, diagnosis and clinical presentation, treatment options (clinical and surgical), and outcomes. VATS (videothoracoscopy sympathectomy) is considered the gold standard for definitive treatment of axillary or palmar hyperhidrosis. Recently, several studies have shown the usefulness of clinical treatment with oxybutynin hydrochloride, leading to clinical improvement of HH in more than 70% of users. Both clinical and surgical treatment of craniofacial hyperhidrosis have good results. However, surgical treatment of FH is associated with more complications. Clinical treatment with oxybutynin hydrochloride yields good results and can be the first therapeutic option. When the patient is not satisfied with this treatment and has good clinical conditions, surgical treatment can be used safely.
A hiperidrose (HH) é caracterizada por transpiração além da quantidade necessária para manter a regulação térmica e as necessidades fisiológicas do corpo. Aproximadamente 9,41% dos indivíduos com HH apresentam hiperidrose craniofacial (FH). Este estudo tem como objetivo revisar os dados mais atuais da literatura sobre FH, incluindo fisiopatologia, diagnóstico e apresentação clínica, opções de tratamento (clínico e cirúrgico) e desfechos. A simpatectomia por videotoracoscopia (VATS) é considerada o padrão-ouro para o tratamento definitivo da hiperidrose axilar ou palmar. Recentemente, vários estudos demonstraram a utilidade do tratamento clínico com cloridrato de oxibutinina, que leva à melhora clínica da HH em mais de 70% dos pacientes. O tratamento clínico e o cirúrgico apresentam bons resultados no tratamento da FH. No entanto, o tratamento cirúrgico da FH apresenta mais complicações. O tratamento clínico com cloridrato de oxibutinina fornece bons resultados e pode ser a primeira opção terapêutica. Quando o paciente não está satisfeito com esse tratamento e mostra boas condições clínicas, o tratamento cirúrgico pode ser usado com segurança.
Keywords: hyperhidrosis; oxybutynin; sympathectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: No conflicts of interest declared concerning the publication of this article.
Figures
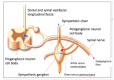

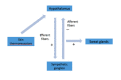
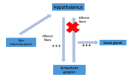

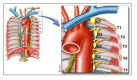
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
