A successful case of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19: walking home without oxygen supplementation
- PMID: 34211653
- PMCID: PMC8221150
- DOI: 10.1080/20009666.2021.1918442
A successful case of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19: walking home without oxygen supplementation
Abstract
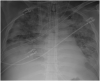
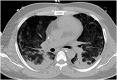
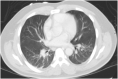
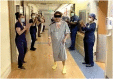
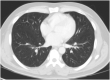
Introduction: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) emerged from Wuhan, China in December 2019 and is the strain of coronavirus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Approximately one-third of the patients with COVID-19 require intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and almost 30% of the patients develop acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is used as salvage therapy for severe ARDS. The role of ECMO in the treatment of COVID-19 remains unclear, although there is emerging evidence that this approach may be an effective salvage therapy for severe ARDS. Case Presentation: We present a case of a previously healthy 39-year-old Hispanic male who presented to the hospital with flu-like symptoms, including headache, fatigue, and myalgia for 8 days in late April 2020. He denied dyspnea on exertion. The patient's symptoms progressed, resulting in pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The patient was managed with prone positioning, convalescent plasma and veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV-ECMO) for 35 days. The patient successfully recovered and was able to ambulate independently and was discharged home from an acute care hospital without oxygen supplementation on hospital day 63. Conclusion: We present one of the first few documented cases of ECMO for severe ARDS due to COVID-19. After a prolonged hospital course requiring VV-ECMO, the patient was discharged home from an acute care hospital without oxygen requirement and ambulated independently, likely as a result of daily aggressive mobility-focused rehabilitation.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; acute respiratory distress syndrome; ambulation; discharge home; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; respiratory failure.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group on behalf of Greater Baltimore Medical Center.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- COVID-19 dashboard by the centers for systems science and engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University. Available from: https://www.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594740fd4029942....
-
- Australia and New Zealand Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ANZ ECMO) Influenza Investigators . Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for 2009 influenza A(H1N1) acute respiratory distress syndrome. JAMA. 2009;302(17):1888–1895. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization: clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected. Available from: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/clinical-management....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
