Agreement Between Trend-Based and Qualitative Analysis of the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness for Glaucoma Progression on Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
- PMID: 34212312
- PMCID: PMC8319289
- DOI: 10.1007/s40123-021-00355-0
Agreement Between Trend-Based and Qualitative Analysis of the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness for Glaucoma Progression on Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
Abstract
Introduction: To evaluate the agreement between trend-based analysis and qualitative assessment of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness for glaucomatous progression on spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SDOCT).
Methods: Retrospective review of 190 eyes from 103 patients with glaucoma or suspected glaucoma that underwent SDOCT imaging during four consecutive clinic visits. Trend-based progression was characterized by a significantly negative slope. Progression by qualitative analysis was determined by review of raw SDOCT B-scans.
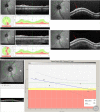
Results: The slope was significantly greater in those with progression than without progression for both trend-based and qualitative analysis (p < 0.001). However, the qualitative grading classified a significantly greater proportion of eyes as progressing compared to trend-based analysis in both the superotemporal (ST) (23.2% vs. 10.5%, p = 0.001) and inferotemporal (IT) RNFL (27.4% vs 8.4%, p < 0.001). The trend-based and qualitative classifications of progression showed poor agreement in both the ST (kappa = 0.0135) and IT RNFL (kappa = 0.1222). The agreement between trend-based and qualitative analysis was lower for eyes with artifacts (ST = 58.11%; IT = 68.7%) than those without artifacts (ST = 80.2%; IT = 74.8%). Moreover, among eyes with artifacts, there was no significant difference in slope between those qualitatively categorized as progressing versus not progressing (p > 0.05).
Conclusions: Poor agreement was found between a trend-based and qualitative analysis of change in RNFL on SDOCT. Careful qualitative review of SDOCT imaging may identify specific areas of glaucoma progression not captured by trend-based methods, especially in the presence of artifacts. Such an approach may also prove useful for detecting glaucoma progression in a clinical setting when there are few data points available.
Keywords: Glaucoma progression; Qualitative; Retinal nerve fiber layer; Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography; Trend-based.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of Artifacts From Optical Coherence Tomography Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer and Macula Scans on Detection of Glaucoma Progression.Am J Ophthalmol. 2021 Jan;221:235-245. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2020.08.018. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Am J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 32818450
-
Retinal nerve fiber layer imaging with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: patterns of retinal nerve fiber layer progression.Ophthalmology. 2012 Sep;119(9):1858-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.03.044. Epub 2012 Jun 5. Ophthalmology. 2012. PMID: 22677426
-
The Influence of Optical Coherence Tomography Measurements of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer on Decision-Making in Glaucoma Diagnosis.Curr Eye Res. 2017 Apr;42(4):575-582. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2016.1220591. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Curr Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 27754717
-
Retinal nerve fiber layer progression in glaucoma: a comparison between retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and retardance.Ophthalmology. 2013 Dec;120(12):2493-2500. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2013.07.027. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Ophthalmology. 2013. PMID: 24053994
-
Diagnosis of glaucoma and detection of glaucoma progression using spectral domain optical coherence tomography.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2013 Mar;24(2):150-61. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0b013e32835d9e27. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 23328662 Review.
Cited by
-
A Response to: Letter to the Editor Regarding "Agreement Between Trend-Based and Qualitative Analysis of the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness for Glaucoma Progression on Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography".Ophthalmol Ther. 2022 Feb;11(1):463-464. doi: 10.1007/s40123-021-00440-4. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Ophthalmol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34870805 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Letter to the Editor Regarding: "Agreement Between Trend-Based and Qualitative Analysis of the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness for Glaucoma Progression on Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography".Ophthalmol Ther. 2022 Feb;11(1):459-461. doi: 10.1007/s40123-021-00438-y. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Ophthalmol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34870804 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

