Clinical and pathohistological characteristics of Alport spectrum disorder caused by COL4A4 mutation c.193-2A>C: a case series
- PMID: 34212557
- PMCID: PMC8275942
- DOI: 10.3325/cmj.2021.62.204
Clinical and pathohistological characteristics of Alport spectrum disorder caused by COL4A4 mutation c.193-2A>C: a case series
Abstract
Aim: To present the pathohistological and clinical characteristics of five Croatian families with Alport spectrum disorders caused by splice acceptor pathogenic variant c.193-2A>C in COL4A4 at the genomic position chr2:227985866.
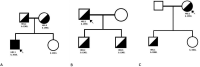
Methods: The study enrolled five probands with kidney biopsy analysis and five family members. Mutation screening was performed with Illumina MiSeq platform. The pathogenic variant was confirmed with standard dye-terminator sequencing.
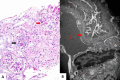
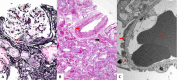
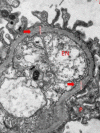
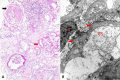
Results: The only homozygous patient, aged two, had proteinuria and hematuria with preserved kidney function and no extrarenal manifestations. This patient had changes characteristic for Alport syndrome observed on electron microscopy of the kidney biopsy. In the heterozygous group, six patients had hematuria, four biopsied probands had proteinuria, and only one had moderately reduced kidney function. Heterozygous probands had variable kidney biopsy findings. Three patients had thin glomerular basement membrane nephropathy visible on electron microscopy and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis on light microscopy, two of them with focal lamellation on electron microscopy. One heterozygous patient had changes characteristic for Alport syndrome on electron microscopy without focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.
Conclusion: The homozygous patient had hematuria and proteinuria with preserved kidney function. The heterozygous patients presented with reasonably mild clinical phenotype and variable pathohistological findings.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Autosomal dominant form of type IV collagen nephropathy exists among patients with hereditary nephritis difficult to diagnose clinicopathologically.Nephrology (Carlton). 2018 Oct;23(10):940-947. doi: 10.1111/nep.13115. Nephrology (Carlton). 2018. PMID: 28704582 Free PMC article.
-
Clinico-pathological correlations in 127 patients in 11 large pedigrees, segregating one of three heterozygous mutations in the COL4A3/ COL4A4 genes associated with familial haematuria and significant late progression to proteinuria and chronic kidney disease from focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009 Sep;24(9):2721-9. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp158. Epub 2009 Apr 8. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009. PMID: 19357112
-
Collagen type IV-related nephropathies in Portugal: pathogenic COL4A3 and COL4A4 mutations and clinical characterization of 25 families.Clin Genet. 2015 Nov;88(5):456-61. doi: 10.1111/cge.12521. Epub 2014 Nov 10. Clin Genet. 2015. PMID: 25307543
-
Thin basement membrane nephropathy.Kidney Int. 2003 Oct;64(4):1169-78. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00234.x. Kidney Int. 2003. PMID: 12969134 Review.
-
Familial hematuria: A review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2017;53(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.medici.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Medicina (Kaunas). 2017. PMID: 28236514 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinicopathological Features of Hereditary Nephritis in the Iranian Population: Analysis of a 14-Year Survey in Kidney Biopsies From a Large Referral Center.Arch Iran Med. 2024 Jan 1;27(1):8-14. doi: 10.34172/aim.2024.02. Arch Iran Med. 2024. PMID: 38431955 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and histopathological characteristics of COL4A3 c.2881+1G>A variant causing Alport spectrum disorders in Croatian population.Biomol Biomed. 2023 Feb 1;23(1):89-100. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2022.7567. Biomol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 35880347 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

