Cangrelor: Clinical Data, Contemporary Use, and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 34212768
- PMCID: PMC8403274
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.121.022125
Cangrelor: Clinical Data, Contemporary Use, and Future Perspectives
Abstract
Cangrelor is the only currently available intravenous platelet P2Y12 receptor inhibitor. It is characterized by potent, predictable, and rapidly reversible antiplatelet effects. Cangrelor has been tested in the large CHAMPION (Cangrelor Versus Standard Therapy to Achieve Optimal Management of Platelet Inhibition) program, where it was compared with different clopidogrel regimens, and it is currently indicated for use in patients with coronary artery disease undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. However, the uptake of cangrelor use varies across the globe and may also include patients with profiles different from those enrolled in the registration trials. These observations underscore the need to fully examine the safety and efficacy of cangrelor in postregistration studies. There are several ongoing and planned studies evaluating the use of cangrelor in real-world practice which will provide important insights to this extent. The current article provides a review on the pharmacology, clinical studies, contemporary use of cangrelor in real-world practice, a description of ongoing studies, and futuristic insights on potential strategies on how to improve outcomes of patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention.
Keywords: acute coronary syndromes; cangrelor; percutaneous coronary intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr De Luca declares that he has received consulting fees or honoraria from Amgen, Aspen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Menarini, Pfizer/Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Sanofi, Servier, and The Medicines Company, outside the present work; Dr Steg declares that he has received consulting fees or honoraria from Amgen, Myokardia, Novo‐Nordisk, and Regeneron, and has received research grants from Amarin, Bayer, Sanofi, and Servier, outside the present work; he has also received payments for participation in clinical trials (Steering Committee, Clinical Events Committee [CEC], Data Safety Monitoring Board [DSMB]) of Amarin, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Idorsia, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Servier. Dr Bhatt discloses the following relationships: Advisory Board: Cardax, CellProthera, Cereno Scientific, Elsevier Practice Update Cardiology, Level Ex, Medscape Cardiology, MyoKardia, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, and Regado Biosciences; Board of Directors: Boston VA Research Institute, Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care, and TobeSoft; Chair: American Heart Association Quality Oversight Committee; Data Monitoring Committees: Baim Institute for Clinical Research (formerly Harvard Clinical Research Institute, for the PORTICO trial, funded by St. Jude Medical, now Abbott), Cleveland Clinic (including for the ExCEED [CENTERA THV System in Intermediate Risk Patients Who Have Symptomatic, Severe, Calcific, Aortic Stenosis Requiring Aortic Valve Replacement] trial, funded by Edwards), Contego Medical (Chair, PERFORMANCE‐II [Protection Against Emboli During Carotid Artery Stenting Using the Neuroguard IEP System]), Duke Clinical Research Institute, Mayo Clinic, Mount Sinai School of Medicine (for the ENVISAGE [Edoxaban Compared to Standard Care After Heart Valve Replacement Using a Catheter in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation] trial, funded by Daiichi Sankyo), Population Health Research Institute; Honoraria: American College of Cardiology (ACC) (Senior Associate Editor, Clinical Trials and News,
Figures
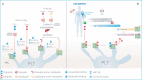


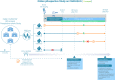

References
-
- De Luca L, Leonardi S, Cavallini C, Lucci D, Musumeci G, Caporale R, Abrignani MG, Lupi A, Rakar S, Gulizia MM, et al. Contemporary antithrombotic strategies in patients with acute coronary syndrome admitted to cardiac care units in Italy: the EYESHOT Study. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2015;4:441–452. DOI: 10.1177/2048872614560505. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

