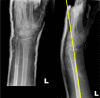
Dorsally displaced distal radius fractures: introduction of Pacetti's line as radiological measurement to predict dorsal fracture displacement
- PMID: 34212906
- PMCID: PMC8343761
- DOI: 10.23750/abm.v92i3.11392
Dorsally displaced distal radius fractures: introduction of Pacetti's line as radiological measurement to predict dorsal fracture displacement
Abstract
Background and aim of the work: In the best of our knowledge there is not yet in the literature a measurement able to assess post reduction stability of distal radius fractures.
Aim: to study the relationship between our newly introduced Pacetti's line, anatomical reduction of DRFs and post-reduction stability of fractures.
Methods: Patients/Participants: 230 patients (122men, 108women) who sustained a dorsally displaced distal radius fracture. Close reduction procedures attempted; below elbow cast applied.
Follow-up: Pacetti's line used on true AP and lateral view xrays after reduction and casting (T0) and at 7-14 days (T1-T2).
Main outcome measurements: Assessment and prediction of early displacement of DRFs.
Results: The Pacetti's line intersected the lunate bone in 162 cases (70.4%) after anatomical reduction, of which 20.4% (N=33) lost anatomical reduction. Cramer's V test: significant relationship between transition of Pacetti's line through the semilunar bone and stability of anatomical reduction at T0 follow-up (p<0.001, Cramer's value=0.83). The Pacetti's line intersected the lunate bone in 119 cases (51.7%) at 7-14 days follow-up. None of patients lost anatomical reduction. Cramer's V test: significant relationship between transition of Pacetti's line through the semilunar bone and stability anatomical reduction at T1 and T2 follow-up (p<0.001, Cramer's value=0.73).
Conclusions: We strongly recommend the use of the Pacetti's line as it seems to provide reliable prediction of further fracture displacement and consequently of definitive management. The Pacetti's line seems to represent a very useful tool providing simple, feasible, efficient and reliable information on DRFs characteristics and natural course.
Conflict of interest statement
Each author declares that he or she has no commercial associations (e.g. consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangement etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous