Endovascular treatment of chronic hemoptysis in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis
- PMID: 34212920
- PMCID: PMC8343743
- DOI: 10.23750/abm.v92i3.10648
Endovascular treatment of chronic hemoptysis in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis
Abstract
Background: We aimed to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of bronchial artery embolization (BAE) in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis in the planned management of "mild" hemoptysis. This treatment, already widely documented and used as a life-saving therapy in an emergency regimen, if properly planned in poorly controlled patients through medical therapy alone, can provide a valid opportunity by reducing the frequency and extent of non-fatal bleeding, but which still worsen the quality of life of these already significantly traumatized patients.
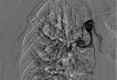
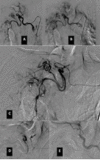
Methods: All procedures were conducted through a right common femoral access with a 5 Fr catheter and a 2.7 Fr super-selective catheter coaxial technique of the branches of the bronchial arteries with suspected bleeding sources. Embolizations were performed with 500-700 micron Terumo PVA plastic microparticles. We decided to adopt the following inclusion criteria for the selection of patients to be enrolled: documented diagnosis of pulmonary TB, the presence of at least one bleeding episode that required at least two blood transfusions, evaluation with bronchoscopic examination to ascertain the bronchial origin of bleeding and the affected lobar site, execution of an angio-ct radiological study for the evaluation of the bronchial systemic anatomy as well as the patency of the pulmonary arterial circulation, general hemodynamic compensation and an age of enrollment between 25 and 65 years.
Results: All selective embolization interventions demonstrated a technical success of 100% of the total number of patients. 11 out of 12 patients did not show any signs of relapse or complications related to the interventional procedure at a first check-up carried out at 48 hours, instead a fatal massive hemoptysis occurred in only one patient. At the next three-month follow-up, no relapses were documented in all selected patients. Only one patient required a second embolization four months after the first procedure.
Conclusions: Radiological-interventional approach in the elective regimen of super-selective embolization of the bronchial arteries (BAE) in the management and control of "mild" hemoptysis in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis not controlled exclusively by medical therapy, according to a strategy systematic of planned intervention and respecting clear and standardized inclusion criteria, represented in our experience a safe and effective procedure, free from significant short and long term complications, especially in well selected patients, which, although not always allows a definitive and stable control of hemoptysis, can in any case significantly limit the risks, also allowing a better planning of the most appropriate therapeutic intervention strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
Each author declares that he or she has no commercial associations (e.g. consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangement etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Similar articles
-
[Expert consensus on operational procedures for bronchial artery embolization in the treatment of hemoptysis].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2025 May 12;48(5):408-417. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20250104-00009. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40300866 Chinese.
-
Immediate and long-term outcomes of endovascular treatment for massive hemoptysis.Int Angiol. 2016 Oct;35(5):469-76. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Int Angiol. 2016. PMID: 26221976
-
Radiologic management of haemoptysis: diagnostic and interventional bronchial arterial embolisation.Rofo. 2015 Apr;187(4):248-59. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1385457. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Rofo. 2015. PMID: 25372159 Review.
-
[The long-term effect and associated factors of double embolization of bronchial artery in patients with lung tuberculosis and hemoptysis].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2004 Jul;27(7):442-5. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15312554 Chinese.
-
Radiological management of hemoptysis: a comprehensive review of diagnostic imaging and bronchial arterial embolization.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010 Apr;33(2):240-50. doi: 10.1007/s00270-009-9788-z. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010. PMID: 20058006 Review.
Cited by
-
Bronchial Artery Embolization.Semin Intervent Radiol. 2022 Aug 31;39(3):210-217. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1751293. eCollection 2022 Jun. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2022. PMID: 36062235 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kalva S. P Bronchial Artery Embolization. Techniques in Vascular and Interventional Radiology. 2009;12:130–138. - PubMed
-
- Butler J. Bronchial circulation: lung biology in healthand disease. 57:725–731.
-
- Cauldwell EW, Siekert RG, Lininger RE, Anson BJ. Thebronchial arteries: an anatomic study in 150 human cadavers. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1948;86:395–412. - PubMed
-
- Kevin Davidson, Samira Shojaee. Managing Massive Hemoptysis. Chest. 2020;157:77–88. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous