A Clinical Prediction Model for Unsuccessful Pulmonary Tuberculosis Treatment Outcomes
- PMID: 34214166
- PMCID: PMC8946703
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciab598
A Clinical Prediction Model for Unsuccessful Pulmonary Tuberculosis Treatment Outcomes
Abstract
Background: Despite widespread availability of curative therapy, tuberculosis (TB) treatment outcomes remain suboptimal. Clinical prediction models can inform treatment strategies to improve outcomes. Using baseline clinical data, we developed a prediction model for unsuccessful TB treatment outcome and evaluated the incremental value of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-related severity and isoniazid acetylator status.
Methods: Data originated from the Regional Prospective Observational Research for Tuberculosis Brazil cohort, which enrolled newly diagnosed TB patients in Brazil from 2015 through 2019. This analysis included participants with culture-confirmed, drug-susceptible pulmonary TB who started first-line anti-TB therapy and had ≥12 months of follow-up. The end point was unsuccessful TB treatment: composite of death, treatment failure, regimen switch, incomplete treatment, or not evaluated. Missing predictors were imputed. Predictors were chosen via bootstrapped backward selection. Discrimination and calibration were evaluated with c-statistics and calibration plots, respectively. Bootstrap internal validation estimated overfitting, and a shrinkage factor was applied to improve out-of-sample prediction. Incremental value was evaluated with likelihood ratio-based measures.
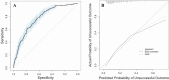
Results: Of 944 participants, 191 (20%) had unsuccessful treatment outcomes. The final model included 7 baseline predictors: hemoglobin, HIV infection, drug use, diabetes, age, education, and tobacco use. The model demonstrated good discrimination (c-statistic = 0.77; 95% confidence interval, .73-.80) and was well calibrated (optimism-corrected intercept and slope, -0.12 and 0.89, respectively). HIV-related factors and isoniazid acetylation status did not improve prediction of the final model.
Conclusions: Using information readily available at treatment initiation, the prediction model performed well in this population. The findings may guide future work to allocate resources or inform targeted interventions for high-risk patients.
Keywords: HIV coinfection; epidemiologic research; prediction model; prognosis; pulmonary tuberculosis.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2020. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2020.
-
- World Health Organization. The End TB Strategy. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

