B Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: From Disease Mechanisms to Targeted Therapies
- PMID: 34215370
- PMCID: PMC8357318
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rdc.2021.04.006
B Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: From Disease Mechanisms to Targeted Therapies
Abstract
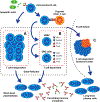
B cells exert a prominent contribution to the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Here, we review the immune mechanisms underlying autoreactive B cell activation in SLE, focusing on how B cell receptor and Toll-like receptor signals integrate to drive breaks in tolerance to nuclear antigens. In addition, we discuss autoantibody-dependent and autoantibody-independent B cell effector functions during lupus pathogenesis. Finally, we address efforts to target B cells therapeutically in human SLE. Despite initial disappointing clinical trials testing B cell depletion in lupus, more recent studies show promise, emphasizing how greater understanding of underlying immune mechanisms can yield clinical benefits.
Keywords: Autoantibodies; B cell depletion; B cells; BAFF; Belimumab; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors have no disclosures.
Figures


References
-
- Navarra SV, Guzman RM, Gallacher AE, et al.Efficacy and safety of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011;377(9767):721–731. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

