Quality of life in patients with IBD during the COVID-19 pandemic in the Netherlands
- PMID: 34215570
- PMCID: PMC8257293
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgast-2021-000670
Quality of life in patients with IBD during the COVID-19 pandemic in the Netherlands
Abstract
Objective: COVID-19 has put a strain on regular healthcare worldwide. For inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), gastrointestinal surgeries were postponed and changes in treatment and diagnostic procedures were made. As abrupt changes in treatment regimens may result in an increased morbidity and consequent well-being of patients with IBD, the aim of this study was to determine the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in patients with IBD.
Design: All patients with IBD who completed both Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire (IBDQ) and 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) questionnaire between 31 August and 13 September 2020 were included in our cohort study. The primary end point was to determine the HRQoL in patients with IBD, measured by the IBDQ and SF-36 questionnaire. The secondary end point was determining which factors influence the HRQoL in patients with IBD.
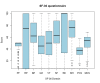
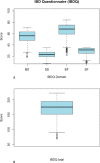
Results: 582 patients with IBD filled in the IBDQ and SF-36 questionnaire. The HRQoL in our study population was low according to the questionnaires on both physical and mental subscales. In addition, multivariate analysis showed that increased age, female sex and patients who underwent surgery had a significantly lower HRQoL, most frequently on the physical domains in both questionnaires.
Conclusion: Patients with IBD had an overall low HRQoL during the COVID-19 pandemic. Furthermore, older patients, women and patients who underwent surgical procedures had the lowest physical HRQoL.
Keywords: COVID-19; inflammatory bowel disease; quality of life.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- NVVH . Handle for surgical procedures during corona crisis, 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
