Thrombocytopenia Induced by Polysulfone Dialysis Membranes
- PMID: 34215716
- PMCID: PMC8265686
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.932045
Thrombocytopenia Induced by Polysulfone Dialysis Membranes
Abstract
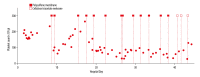
BACKGROUND Biocompatible hemodialysis membranes have greatly advanced the treatment of renal failure. Synthetic polysulfone dialysis membranes are considered to be very biocompatible because of their low propensity to activate complement. However, these membranes can reduce platelet count through platelet activation, although the mechanism of this activation is unknown. CASE REPORT We report the case of an 82-year-old man with a history of chronic kidney disease with recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding and worsening renal function who was initiated on renal replacement therapy with polysulfone dialysis membranes. On admission, the patient's platelet count was normal at 233×10³/μL. A significant fall in platelet count was observed following most dialysis treatments, reaching a nadir of 37×10³/μL. With occasional dialysis treatments, his platelet count did not change. This dialysis-induced thrombocytopenia resolved following substitution with Cellentia-H cellulose triacetate single-use, hollow-fiber, high-flux hemodialyzer membrane. CONCLUSIONS Polysulfone membranes are capable of activating platelets, which can result in severe thrombocytopenia. However, the magnitude of dialysis-induced thrombocytopenia varies from treatment to treatment. As such, it may not be evident when the pre- and postdialysis platelet counts are measured for a single treatment. Because the etiology of this platelet activation is unknown, substitution with cellulose triacetate membranes should be considered. These membranes have an unrelated chemical composition and a very low propensity to activate platelets.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Ferreira JA, Johnson DW. The incidence of thrombocytopenia associated with continuous renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients. Ren Fail. 2015;37(7):1232–36. - PubMed
-
- Hoenich NA, Woffindin C, Mathews JN, Vienken J. Biocompatibility of membranes used in the treatment of renal failure. Biomaterials. 1995;16(8):587–92. - PubMed
-
- Posadas MA, Hahn D, Schleuter W, Paparello J. Thrombocytopenia associated with dialysis treatments. Hemodial Int. 2011;15(3):416–23. - PubMed
-
- Daugirdas JT, Bernardo AA. Hemodialysis effect on platelet count and function and hemodialysis-associated thrombocytopenia. Kidney Int. 2012;82(2):147–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

