Polyamine metabolism is a central determinant of helper T cell lineage fidelity
- PMID: 34216540
- PMCID: PMC8358979
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.007
Polyamine metabolism is a central determinant of helper T cell lineage fidelity
Abstract
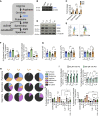
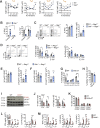
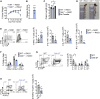
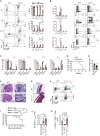
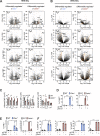
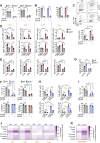
Polyamine synthesis represents one of the most profound metabolic changes during T cell activation, but the biological implications of this are scarcely known. Here, we show that polyamine metabolism is a fundamental process governing the ability of CD4+ helper T cells (TH) to polarize into different functional fates. Deficiency in ornithine decarboxylase, a crucial enzyme for polyamine synthesis, results in a severe failure of CD4+ T cells to adopt correct subset specification, underscored by ectopic expression of multiple cytokines and lineage-defining transcription factors across TH cell subsets. Polyamines control TH differentiation by providing substrates for deoxyhypusine synthase, which synthesizes the amino acid hypusine, and mice in which T cells are deficient for hypusine develop severe intestinal inflammatory disease. Polyamine-hypusine deficiency caused widespread epigenetic remodeling driven by alterations in histone acetylation and a re-wired tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Thus, polyamine metabolism is critical for maintaining the epigenome to focus TH cell subset fidelity.
Keywords: T cells; eIF5A; hypusine; immunity; immunometabolism; metabolism; polyamines.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests E.L.P. is a SAB member of ImmunoMet, a founder of Rheos Medicines, and an advisory board member for Cell.
Figures








Comment in
-
Polyamine: A metabolic compass for T helper cell fate direction.Cell. 2021 Aug 5;184(16):4109-4112. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.07.012. Cell. 2021. PMID: 34358466
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

