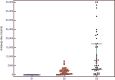
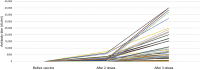
Humoral response after 3 doses of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in patients on hemodialysis
- PMID: 34216675
- PMCID: PMC8243640
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.06.025
Humoral response after 3 doses of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in patients on hemodialysis
Figures

References
-
- Frantzen L, Cavaille G, Thibeaut S, El-Haik Y. Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in a hemodialysis cohort [e-pub ahead of print]. Nephrol Dial Transplant. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfab165. Accessed July 13, 2021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lacson E, Argyropoulos CP, Manley HJ, et al. Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in dialysis [preprint]. medRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.08.21254779. Accessed July 13, 2021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

