"Vitamin D supplementation and COVID-19 treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis"
- PMID: 34217144
- PMCID: PMC8236412
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102189
"Vitamin D supplementation and COVID-19 treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis"
Abstract
Background: Vitamin-D is an immune-modulator which might be linked to disease severity by SARS-CoV-2.
Methods: Meta-analysis of RCTs and quasi-experimental studies, evaluating the role of vitamin-D supplementation in COVID patients was done.
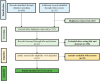
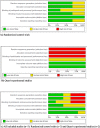
Results: Total 5 studies (3 RCTs and 2 Quasi-experimental) including n = 467 patients were included. Vitamin D didn't reduce mortality (RR 0.55, 95%CI 0.22 to 1.39, p = 0.21), ICU admission rates (RR 0.20, 95% CI 0.01-4.26, p = 0.3) and need for invasive ventilation (RR 0.24, 95% CI 0.01-7.89, p = 0.42).
Conclusion: No significant difference with vitamin-D supplementation on major health related outcomes in COVID-19. Well-designed RCTs are required addressing this topic.
Keywords: COVID pneumonia; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Vitamin-D.
Copyright © 2021 Diabetes India. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Spurious undermining of the adjuvant role of vitamin D in COVID-19.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021 Sep-Oct;15(5):102230. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102230. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021. PMID: 34340050 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Does Vitamin D have a role to play in Covid-19 in the dexamethasone era?Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021 Sep-Oct;15(5):102237. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102237. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021. PMID: 34364302 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. https://covid19.who.int
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

