Model-based meta-analysis of changes in circulatory system physiology in patients with chronic heart failure
- PMID: 34218511
- PMCID: PMC8452295
- DOI: 10.1002/psp4.12676
Model-based meta-analysis of changes in circulatory system physiology in patients with chronic heart failure
Abstract
To characterize and compare various medicines for chronic heart failure (CHF), changes in circulatory physiological parameter during pharmacotherapy were investigated by a model-based meta-analysis (MBMA) of circulatory physiology. The clinical data from 61 studies mostly in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), reporting changes in heart rate, blood pressure, or ventricular volumes after treatment with carvedilol, metoprolol, bisoprolol, bucindolol, enalapril, aliskiren, or felodipine, were analyzed. Seven cardiac and vasculature function indices were estimated without invasive measurements using models based on appropriate assumptions, and their correlations with the mortality were assessed. Estimated myocardial oxygen consumption, a cardiac load index, correlated excellently with the mortality at 3, 6, and 12 months after treatment initiation, and it explained differences in mortality across the different medications. The analysis based on the present models were reasonably consistent with the hypothesis that the treatment of HFrEF with various medications is due to effectively reducing the cardiac load. Assessment of circulatory physiological parameters by using MBMA would be insightful for quantitative understanding of CHF treatment.
© 2021 The Authors. CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Y.S. is an employee of Sanofi K.K. However, Sanofi K.K. is not involved in this analysis. S.G. was involved in this study before she joined Astellas Pharma Inc. All other authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures

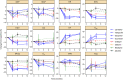
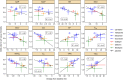

References
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA Focused Update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. Circulation. 2017;136:e137‐e161. - PubMed
-
- Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:3021‐3104. - PubMed
-
- Poole‐Wilson PA, Swedberg K, Cleland JGF, et al. Comparison of carvedilol and metoprolol on clinical outcomes in patients with chronic heart failure in the Carvedilol Or Metoprolol European Trial (COMET): randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;362:7‐13. - PubMed
-
- MERIT‐HF Study Group . Effect of metoprolol CR/XL in chronic heart failure: metoprolol CR/XL randomised intervention trial in congestive heart failure (MERIT‐HF). Lancet. 1999;353:2001‐2007. - PubMed
-
- CIBIS‐II Investigators and Committees . The Cardiac Insufficiency Bisoprolol Study II (CIBIS‐II): a randomised trial. Lancet. 1999;353:9‐13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

