Improved oxygenation with inhaled milrinone in mechanically ventilated patients with severe COVID-19
- PMID: 34218906
- PMCID: PMC8185181
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bja.2021.06.002
Improved oxygenation with inhaled milrinone in mechanically ventilated patients with severe COVID-19
Keywords: COVID-19; acute respiratory distress syndrome; hypoxaemia; milrinone; phosphodiesterase 3 inhibitor; pulmonary vasodilator.
Figures
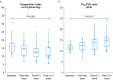
References
-
- The Faculty of Intensive Care Medicine (FICM) and The Intensive Care Society (ICS). Clinical guide for the management and care of critically ill adults with COVID-19 during the coronavirus pandemic. Available from: https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5e6613a1dc75b87df82b78e1/t/60800b... (accessed 1 May 2021).
-
- Haraldsson S.A., Kieler-Jensen N., Ricksten S.E. The additive pulmonary vasodilatory effects of inhaled prostacyclin and inhaled milrinone in postcardiac surgical patients with pulmonary hypertension. Anesth Analg. 2001;93:1439–1445. - PubMed
-
- Theodoraki K., Thanopoulos A., Rellia P., et al. A retrospective comparison of inhaled milrinone and iloprost in post-bypass pulmonary hypertension. Heart Vessels. 2017;32:1488–1497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

