Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of the Human Endometrial Fluid during the Natural Cycle
- PMID: 34220191
- PMCID: PMC8221874
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8849664
Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of the Human Endometrial Fluid during the Natural Cycle
Abstract
Purpose: Some microbiota patterns have been associated with favorable IVF prognosis and others with pathological conditions. The endometrial fluid aspirate (EFA) contains antibacterial proteins that are enriched in implantative IVF cycles, but the antimicrobial effect of EFA has not been addressed. We aimed to evaluate the antimicrobial activity of the human endometrial fluid during the natural cycle.
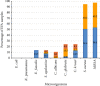
Methods: EFA was obtained through an embryo transfer catheter in 38 women, aged 18-40 years, with regular cycles attending to a fertility clinic. The antimicrobial activity of EFAs was tested against two strains of Staphylococcus aureus; one strain each of Streptococcus agalactiae, Enterococcus faecalis, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella pneumoniae; and three yeasts (Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, and Candida krusei).
Results: All samples exhibited antibacterial activity against S. aureus. In addition, 32.4% of EFAs were active against one of the other microorganisms assayed, 16.2% against two, and 5.4% against four of them. In contrast, none exhibited antibacterial activity against E. coli or K. pneumoniae. The antimicrobial activity differs considerably between EFA samples, and we failed to observe a cycle-related pattern.
Conclusions: EFA presented two antimicrobial activity patterns: (a) one common to all the samples, exhibiting activity against S. aureus and lack of activity against E. coli and K. pneumoniae, and (b) an individualized pattern, showing activity against some of the other microorganisms tested. The intensity of antibacterial activity differs between EFA samples. Our data suggest that the uterine microbiota is controlled by means of endometrial fluid components.
Copyright © 2021 Marta Bregón-Villahoz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Friedenthal J., Maxwell S. M., Munné S., et al. Next generation sequencing for preimplantation genetic screening improves pregnancy outcomes compared with array comparative genomic hybridization in single thawed euploid embryo transfer cycles. Fertility and Sterility. 2018;109(4):627–632. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.12.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Noyes R. W., Hertig A. T., Rock J. Dating the endometrial biopsy. Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey. 1950;5(4):561–564. doi: 10.1097/00006254-195008000-00044. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases