Enhancement of cytotoxicity and induction of apoptosis by cationic nano-liposome formulation of n-butylidenephthalide in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 34220320
- PMCID: PMC8241786
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.51439
Enhancement of cytotoxicity and induction of apoptosis by cationic nano-liposome formulation of n-butylidenephthalide in breast cancer cells
Abstract
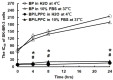
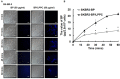
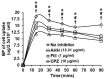
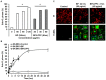
Breast cancer is the second most common malignancy in women. Current clinical therapy for breast cancer has many disadvantages, including metastasis, recurrence, and poor quality of life. Furthermore, it is necessary to find a new therapeutic drug for breast cancer patients to meet clinical demand. n-Butylidenephthalide (BP) is a natural and hydrophobic compound that can inhibit several tumors. However, BP is unstable in aqueous or protein-rich environments, which reduces the activity of BP. Therefore, we used an LPPC (Lipo-PEG-PEI complex) that can encapsulate both hydrophobic and hydrophilic compounds to improve the limitation of BP. The purpose of this study is to investigate the anti-tumor mechanisms of BP and BP/LPPC and further test the efficacy of BP encapsulated by LPPC on SK-BR-3 cells. BP inhibited breast cancer cell growth, and LPPC encapsulation (BP/LPPC complex) enhanced the cytotoxicity on breast cancer by stabilizing the BP activity and offering endocytic pathways. Additionally, BP and LPPC-encapsulated BP induced cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase and might trigger both extrinsic as well as intrinsic cell apoptosis pathway, resulting in cell death. Moreover, the BP/LPPC complex had a synergistic effect with doxorubicin of enhancing the inhibitory effect on breast cancer cells. Consequently, LPPC-encapsulated BP could improve the anti-cancer effects on breast cancer in vitro. In conclusion, BP exhibited an anti-cancer effect on breast cancer cells, and LPPC encapsulation efficiently improved the cytotoxicity of BP via an acceleration of entrapment efficiency to induce cell cycle block and apoptosis. Furthermore, BP/LPPC exhibited a synergistic effect in combination with doxorubicin.
Keywords: Cell apoptosis; Cell cycle; Polycationic liposome containing PEI and polyethylene glycol complex (LPPC); Synergistic effect; n-Butylidenephthalide (BP).
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Antitumor Effect of n-Butylidenephthalide Encapsulated on B16/F10 Melanoma Cells In Vitro with a Polycationic Liposome Containing PEI and Polyethylene Glycol Complex.Molecules. 2018 Dec 6;23(12):3224. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123224. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30563276 Free PMC article.
-
Encapsulated n-Butylidenephthalide Efficiently Crosses the Blood-Brain Barrier and Suppresses Growth of Glioblastoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Jan 31;15:749-760. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S235815. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32099363 Free PMC article.
-
Liposomal n-butylidenephthalide protects the drug from oxidation and enhances its antitumor effects in glioblastoma multiforme.Int J Nanomedicine. 2015 Sep 28;10:6009-20. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S85790. eCollection 2015. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 26451107 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor Effects of N-Butylidenephthalide Encapsulated in Lipopolyplexs in Colorectal Cancer Cells.Molecules. 2020 May 21;25(10):2394. doi: 10.3390/molecules25102394. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32455622 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive constituents of animal-derived traditional Chinese medicinal materials for breast cancer: opportunities and challenges.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022 Jul 15;23(7):547-563. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2101019. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022. PMID: 35794685 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) upregulated by n-butylidenephthalide via the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway ameliorates drug-induced gingival enlargement.Biofactors. 2024 Nov-Dec;50(6):1192-1207. doi: 10.1002/biof.2077. Epub 2024 May 22. Biofactors. 2024. PMID: 38777369 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria-Targeted Lipid Nanoparticles Loaded with Rotenone as a New Approach for the Treatment of Oncological Diseases.Molecules. 2023 Oct 23;28(20):7229. doi: 10.3390/molecules28207229. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37894708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Kelloff GJ, Crowell JA, Steele VE, Lubet RA, Malone WA, Boone CW. et al. Progress in cancer chemoprevention: development of diet-derived chemopreventive agents. J Nutr. 2000;130:467S–71S. - PubMed
-
- Sporn MB, Newton DL. Chemoprevention of cancer with retinoids. Fed Proc. 1979;38:2528–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

