Inferior Frontal Gyrus-Based Resting-State Functional Connectivity and Medium Dispositional Use of Reappraisal Strategy
- PMID: 34220436
- PMCID: PMC8248357
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2021.681859
Inferior Frontal Gyrus-Based Resting-State Functional Connectivity and Medium Dispositional Use of Reappraisal Strategy
Abstract
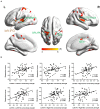
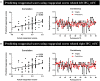
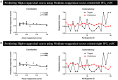
The previous neuroimaging functional connectivity analyses have indicated that the association between the inferior frontal gyrus (IFG) and other brain regions results in better emotion regulation in reappraisal tasks. However, no study has explored the relationship between IFG-based resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC) and the dispositional use of reappraisal strategy. Therefore, the present study examined the potential associations between rsFC patterns of both left and right IFG and dispositional reappraisal use. One hundred healthy participants completed the Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (ERQ) and underwent a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) acquisition. An approach of the seed-based rsFC analysis was recruited to estimate the functional connectivity maps of bilateral IFG with other brain regions, and the reappraisal scores from the ERQ were then correlated with the functional maps. Our findings showed that IFG-based rsFC was positively correlated with dispositional reappraisal only in the range of 4 to 5.5 points [medium reappraisal group (MRG)]. Specifically, medium dispositional reappraisal was positively correlated with rsFC between left/right IFG and bilateral temporal gyrus. Besides, medium dispositional reappraisal was positively correlated with rsFC between left IFG and bilateral superior parietal lobe (SPL), middle cingulate cortex (MCC), and right insula, as well as between right IFG and dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (DMPFC) and anterior cingulate cortex (ACC). In conclusion, these results indicate that bilateral IFG plays an important role in the medium use of the reappraisal strategy.
Keywords: emotion regulation; inferior frontal gyrus; medium reappraisal; prediction; resting-state functional connectivity.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Xie, Ngetich, Zhang, Jin and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Connectivity pattern differences bilaterally in the cerebellum posterior lobe in healthy subjects after normal sleep and sleep deprivation: a resting-state functional MRI study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015 May 26;11:1279-89. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S84204. eCollection 2015. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015. PMID: 26064046 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of acupuncture on pain-emotion related brain regions in patients with cervical spondylosis of cervical type: a fMRI study].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2021 Aug 12;41(8):906-12. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20201022-k0007. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2021. PMID: 34369703 Chinese.
-
Brain functional connectivity during storage based on resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging with synchronous urodynamic testing in healthy volunteers.Brain Imaging Behav. 2021 Jun;15(3):1676-1684. doi: 10.1007/s11682-020-00362-y. Brain Imaging Behav. 2021. PMID: 32725470
-
Functional and structural brain differences in bipolar disorder: a multimodal meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies.Psychol Med. 2022 Oct;52(14):2861-2873. doi: 10.1017/S0033291722002392. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Psychol Med. 2022. PMID: 36093787 Review.
-
A multimodal meta-analysis of regional functional and structural brain abnormalities in obsessive-compulsive disorder.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024 Feb;274(1):165-180. doi: 10.1007/s00406-023-01594-x. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 37000246
Cited by
-
Altered functional connectivity strength in chronic insomnia associated with gut microbiota composition and sleep efficiency.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Nov 22;13:1050403. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1050403. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36483137 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced resting-state functional connectivity between insula and inferior frontal gyrus and superior temporal gyrus in hoarding disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 19;15:1399062. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1399062. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38966185 Free PMC article.
-
Severity of alcohol use disorder influences sex differences in sleep, mood, and brain functional connectivity impairments.Brain Commun. 2022 May 22;4(4):fcac127. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac127. eCollection 2022. Brain Commun. 2022. PMID: 35794873 Free PMC article.
-
CNS imaging characteristics in fibromyalgia patients with and without peripheral nerve involvement.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 25;12(1):6707. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10489-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35469050 Free PMC article.
-
Lower functional connectivity state transitions during affective processing correlate with subsequent impairment in sustaining positive affect in subthreshold depression.Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2025 Jan-Mar;25(1):100560. doi: 10.1016/j.ijchp.2025.100560. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40206962 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

