Neuropharmacological Effects of Quercetin: A Literature-Based Review
- PMID: 34220504
- PMCID: PMC8248808
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.665031
Neuropharmacological Effects of Quercetin: A Literature-Based Review
Abstract
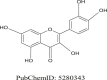
Quercetin (QUR) is a natural bioactive flavonoid that has been lately very studied for its beneficial properties in many pathologies. Its neuroprotective effects have been demonstrated in many in vitro studies, as well as in vivo animal experiments and human trials. QUR protects the organism against neurotoxic chemicals and also can prevent the evolution and development of neuronal injury and neurodegeneration. The present work aimed to summarize the literature about the neuroprotective effect of QUR using known database sources. Besides, this review focuses on the assessment of the potential utilization of QUR as a complementary or alternative medicine for preventing and treating neurodegenerative diseases. An up-to-date search was conducted in PubMed, Science Direct and Google Scholar for published work dealing with the neuroprotective effects of QUR against neurotoxic chemicals or in neuronal injury, and in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Findings suggest that QUR possess neuropharmacological protective effects in neurodegenerative brain disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Amyloid β peptide, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, multiple sclerosis, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. In summary, this review emphasizes the neuroprotective effects of QUR and its advantages in being used in complementary medicine for the prevention and treatment o of different neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: mechanisms; neural damage; neurodegenerative disorders; neuropharmacological effects; quercetin; signaling pathways.
Copyright © 2021 Islam, Quispe, Hossain, Islam, Al-Harrasi, Al-Rawahi, Martorell, Mamurova, Seilkhan, Altybaeva, Abdullayeva, Docea, Calina and Sharifi-Rad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Natural Products and Their Bioactive Compounds: Neuroprotective Potentials against Neurodegenerative Diseases.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Feb 14;2020:6565396. doi: 10.1155/2020/6565396. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32148547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of biological effects of Quercetin on ovary.Phytother Res. 2021 Jan;35(1):33-49. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6750. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Phytother Res. 2021. PMID: 32557927 Review.
-
Effect of quercetin-loaded poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid nanoparticles on lipopolysaccharide-induced memory decline, oxidative stress, amyloidogenesis, neurotransmission, and Nrf2/HO-1 expression.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 10;10(1):e23527. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23527. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38169932 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential and Clinical Evidence of Hesperidin as Neuroprotective Agent.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(1):5-14. doi: 10.2174/1871524922666220404164405. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35379141
-
The Role of Vitamins in Neurodegenerative Disease: An Update.Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 22;9(10):1284. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101284. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34680401 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-Target Mechanisms of Phytochemicals in Alzheimer's Disease: Effects on Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation and Protein Aggregation.J Pers Med. 2022 Sep 15;12(9):1515. doi: 10.3390/jpm12091515. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36143299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anxiolytic-like Effect of Quercetin Possibly through GABA Receptor Interaction Pathway: In Vivo and In Silico Studies.Molecules. 2022 Oct 22;27(21):7149. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217149. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36363979 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of the ameliorative efficacy of Catharanthus roseus extract against Cd2+ toxicity: implications for human health and remediation strategies.Front Public Health. 2024 Mar 8;12:1327611. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1327611. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38525339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin and Its Nano-Formulations for Brain Tumor Therapy-Current Developments and Future Perspectives for Paediatric Studies.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 16;15(3):963. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030963. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytates as a natural source for health promotion: A critical evaluation of clinical trials.Front Chem. 2023 Apr 14;11:1174109. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1174109. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 37123871 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdalla F. H., Cardoso A. M., Pereira L. B., Schmatz R., Gonçalves J. F., Stefanello N., et al. (2013). Neuroprotective Effect of Quercetin in Ectoenzymes and Acetylcholinesterase Activities in Cerebral Cortex Synaptosomes of Cadmium-Exposed Rats. Mol. Cel Biochem 381 (1-2), 1–8. 10.1007/s11010-013-1659-x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abdalla F. H., Schmatz R., Cardoso A. M., Carvalho F. B., Baldissarelli J., de Oliveira J. S., et al. (2014). Quercetin Protects the Impairment of Memory and Anxiogenic-like Behavior in Rats Exposed to Cadmium: Possible Involvement of the Acetylcholinesterase and Na+,K+-ATPase Activities. Physiol. Behav. 135, 152–167. 10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.06.008 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

