Pharmacokinetics of Acetaminophen and Metformin Hydrochloride in Rats After Exposure to Simulated High Altitude Hypoxia
- PMID: 34220516
- PMCID: PMC8249799
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.692349
Pharmacokinetics of Acetaminophen and Metformin Hydrochloride in Rats After Exposure to Simulated High Altitude Hypoxia
Abstract
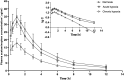
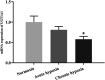
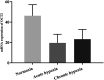
The pharmacokinetic characteristics of drugs were altered under high altitude hypoxia, thereby affecting the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drug. However, there are few literatures on the pharmacokinetic changes of antipyretic and pain-relieving drugs and cardiovascular system drugs at high altitude. This study aimed to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of acetaminophen and metformin hydrochloride in rats under simulated high altitude hypoxia condition. Mechanically, the protein and mRNA expression of uridine diphosphate glucuronyltransferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) and organic cation transporter 2 (OCT2) were investigated by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), respectively. Compared with the normoxia group, the t1/2 and AUC of acetaminophen were significantly increased, and the CL/F was significantly decreased in rats after exposure to simulated high altitude hypoxia. The t1/2 of metformin hydrochloride was significantly increased by simulated high altitude hypoxia. No significant differences in AUC and CL/F of metformin hydrochloride were observed when comparing the hypoxia group with the normoxia group. The protein and mRNA expression of UGT1A1 and OCT2 were decreased significantly under hypoxia in rats. This study found obvious changes in the pharmacokinetics of acetaminophen and metformin hydrochloride in rats after exposure to simulated high altitude hypoxia, and they might be due to significant decreases in the expressions of UGT1A1 and OCT2. To sum up, our data suggested that the pharmacokinetics of acetaminophen and metformin hydrochloride should be reexamined, and the optimal dose should be reassessed under hypoxia exposure.
Keywords: OCT2; UGT1A1; acetaminophen; high altitude hypoxia; metformin hydrochloride; pharmacokinetics.
Copyright © 2021 Zhu, Yang, Nian, Liu, Duan, Bai, Wang, Zhou, Wang, Qu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
High-altitude Hypoxia Influences the Activities of the Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme CYP3A1 and the Pharmacokinetics of Four Cardiovascular System Drugs.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 21;15(10):1303. doi: 10.3390/ph15101303. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297415 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of plateau hypoxia on population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of metformin in patients with Type 2 diabetes.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Apr 28;48(4):481-490. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.220267. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37385610 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Hypoxia Plays a Key Role in the Pharmacokinetic Changes of Drugs at High Altitude.Curr Drug Metab. 2018;19(11):960-969. doi: 10.2174/1389200219666180529112913. Curr Drug Metab. 2018. PMID: 29807512 Review.
-
Regulation of High-Altitude Hypoxia on the Transcription of CYP450 and UGT1A1 Mediated by PXR and CAR.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 17;11:574176. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.574176. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33041817 Free PMC article.
-
MDR1 will play a key role in pharmacokinetic changes under hypoxia at high altitude and its potential regulatory networks.Drug Metab Rev. 2015 May;47(2):191-8. doi: 10.3109/03602532.2015.1007012. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Drug Metab Rev. 2015. PMID: 25639892 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictors of gastrointestinal complaints in patients on metformin therapy.Open Med (Wars). 2023 Nov 29;18(1):20230871. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0871. eCollection 2023. Open Med (Wars). 2023. PMID: 38045859 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of Acipimox in Plasma and Tissues by LC-MS/MS: Application to Pharmacokinetic Comparison between Normoxia and Hypoxia.Molecules. 2022 Sep 28;27(19):6413. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196413. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36234950 Free PMC article.
-
High-altitude Hypoxia Influences the Activities of the Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme CYP3A1 and the Pharmacokinetics of Four Cardiovascular System Drugs.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 21;15(10):1303. doi: 10.3390/ph15101303. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297415 Free PMC article.
-
Space medicine: Hunting for pharmacologist's guide in dealing with drugs in microgravity.Indian J Pharmacol. 2023 Sep-Oct;55(5):281-285. doi: 10.4103/ijp.ijp_591_23. Indian J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37929405 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effects of plateau hypoxia on population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of metformin in patients with Type 2 diabetes.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Apr 28;48(4):481-490. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.220267. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37385610 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

