The Release of Nitric Oxide Is Involved in the β-Arrestin1-Induced Antihypertensive Effect in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla
- PMID: 34220554
- PMCID: PMC8249856
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.694135
The Release of Nitric Oxide Is Involved in the β-Arrestin1-Induced Antihypertensive Effect in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla
Abstract
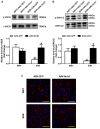
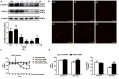
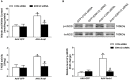
β-Arrestin1 is a multifunctional scaffold protein with the ability to interact with diverse signaling molecules independent of G protein-coupled receptors. We previously reported that overexpression of β-arrestin1 in the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) decreased blood pressure (BP) and renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA) in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs). Nitric oxide (NO) is widely reported to be involved in central cardiovascular regulation. The goal of this study was to investigate whether NO signaling contributes to the β-arrestin1-mediated antihypertensive effect in the RVLM. It was found that bilateral injection of adeno-associated virus containing Arrb1 gene (AAV-Arrb1) into the RVLM of SHRs significantly increased NO production and NO synthase (NOS) activity. Microinjection of the non-selective NOS inhibitor N-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME; 10 nmol) into the RVLM prevented the β-arrestin1-induced cardiovascular inhibitory effect. Furthermore, β-arrestin1 overexpression in the RVLM significantly upregulated the expression of phosphorylated neuronal NOS (nNOS) by 3.8-fold and extracellular regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) by 5.6-fold in SHRs. The β-arrestin1-induced decrease in BP and RSNA was significantly abolished by treatment with ERK1/2 small interfering RNA (ERK1/2 siRNA). Moreover, ERK1/2 siRNA attenuated the β-arrestin1-induced NO production, NOS activity, and nNOS phosphorylation in the RVLM. Taken together, these data demonstrate that the antihypertensive effect of β-arrestin1 in the RVLM is mediated by nNOS-derived NO release, which is associated with ERK1/2 activation.
Keywords: ERK1/2; NO; RVLM; hypertension; β-arrestin1.
Copyright © 2021 Sun, Tan, Ge, Xu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Overexpression of ß-Arrestin1 in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla Downregulates Angiotensin Receptor and Lowers Blood Pressure in Hypertension.Front Physiol. 2018 Mar 28;9:297. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00297. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29643817 Free PMC article.
-
β-Arrestin1 Reduces Oxidative Stress via Nrf2 Activation in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla in Hypertension.Front Neurosci. 2021 Apr 7;15:657825. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.657825. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33897365 Free PMC article.
-
Selective sensitization by nitric oxide of sympathetic baroreflex in rostral ventrolateral medulla of conscious rabbits.Hypertension. 2005 May;45(5):901-6. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000160322.83725.6b. Epub 2005 Mar 7. Hypertension. 2005. PMID: 15753230
-
The interleukin-enhanced binding factor 3-mediated inhibition of nitric oxide production via phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway contributes to central cardiovascular regulation in the rostral ventrolateral medulla in hypertension.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022 Dec 1;323(6):R861-R874. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00019.2022. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36222883
-
Brain stem adenosine receptors modulate centrally mediated hypotensive responses in conscious rats: A review.J Adv Res. 2015 May;6(3):331-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2014.12.005. Epub 2014 Dec 18. J Adv Res. 2015. PMID: 26257930 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microglia-derived TNF-α contributes to RVLM neuronal mitochondrial dysfunction via blocking the AMPK-Sirt3 pathway in stress-induced hypertension.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Jun 1;20(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02818-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 37264405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker B. K., Tian C., Zucker I. H., Wang H. J. (2016). Influence of brain-derived neurotrophic factor-tyrosine receptor kinase B signalling in the nucleus tractus solitarius on baroreflex sensitivity in rats with chronic heart failure. J. Physiol. 594 5711–5725. 10.1113/JP272318 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan J. Y., Cheng H. L., Chou J. L., Li F. C., Dai K. Y., Chan S. H., et al. (2007a). Heat shock protein 60 or 70 activates nitric-oxide synthase (NOS) I- and inhibits NOS II-associated signaling and depresses the mitochondrial apoptotic cascade during brain stem death. J. Biol. Chem. 282 4585–4600. 10.1074/jbc.M603394200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chan S. H., Wang L. L., Tseng H. L., Chan J. Y. (2007b). Upregulation of AT1 receptor gene on activation of protein kinase Cbeta/nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide diphosphate oxidase/ERK1/2/c-fos signaling cascade mediates long-term pressor effect of angiotensin II in rostral ventrolateral medulla. J. Hypertens 25 1845–1861. 10.1097/HJH.0b013e328217b286 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

