Could Exogenous Insulin Ameliorate the Metabolic Dysfunction Induced by Glucocorticoids and COVID-19?
- PMID: 34220705
- PMCID: PMC8249851
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.649405
Could Exogenous Insulin Ameliorate the Metabolic Dysfunction Induced by Glucocorticoids and COVID-19?
Abstract
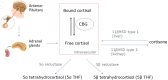
The finding that high-dose dexamethasone improves survival in those requiring critical care due to COVID-19 will mean much greater usage of glucocorticoids in the subsequent waves of coronavirus infection. Furthermore, the consistent finding of adverse outcomes from COVID-19 in individuals with obesity, hypertension and diabetes has focussed attention on the metabolic dysfunction that may arise with critical illness. The SARS coronavirus itself may promote relative insulin deficiency, ketogenesis and hyperglycaemia in susceptible individuals. In conjunction with prolonged critical care, these components will promote a catabolic state. Insulin infusion is the mainstay of therapy for treatment of hyperglycaemia in acute illness but what is the effect of insulin on the admixture of glucocorticoids and COVID-19? This article reviews the evidence for the effect of insulin on clinical outcomes and intermediary metabolism in critical illness.
Keywords: coronavirus – COVID-19; critical-illness; dexamethasone; glucocorticoid; insulin.
Copyright © 2021 Whyte, Vas and Umpleby.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of hyperglycemia, glucocorticoids, and insulin use with morbidity and mortality in the pediatric intensive care unit.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2012 Jan 1;6(1):5-14. doi: 10.1177/193229681200600102. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2012. PMID: 22401317 Free PMC article.
-
[The endocrine and metabolic link between COVID-19, diabetes and obesity].Ugeskr Laeger. 2020 Jul 13;182(29):V05200381. Ugeskr Laeger. 2020. PMID: 32734864 Review. Danish.
-
New Insights on Effects of Glucocorticoids in Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Endocr Pract. 2022 Oct;28(10):1100-1106. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2022.07.006. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Endocr Pract. 2022. PMID: 35870803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Consensus recommendations for the management of hyperglycaemia in critically ill patients in the Indian setting.J Assoc Physicians India. 2014 Jul;62(7 Suppl):16-25. J Assoc Physicians India. 2014. PMID: 25668933 Review.
-
Glucocorticoid-Induced Hyperglycemia: A Neglected Problem.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2024 Apr;39(2):222-238. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2024.1951. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2024. PMID: 38532282 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glycemic control using intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring in patients with diabetes requiring methylprednisolone therapy for severe COVID-19.Glob Health Med. 2022 Dec 31;4(6):336-340. doi: 10.35772/ghm.2022.01053. Glob Health Med. 2022. PMID: 36589220 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

