COVID-19 and Diabetes: Understanding the Interrelationship and Risks for a Severe Course
- PMID: 34220706
- PMCID: PMC8247904
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.649525
COVID-19 and Diabetes: Understanding the Interrelationship and Risks for a Severe Course
Abstract
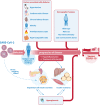
The relationship between COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus is complicated and bidirectional. On the one hand, diabetes mellitus is considered one of the most important risk factors for a severe course of COVID-19. Several factors that are often present in diabetes mellitus are likely to contribute to this risk, such as older age, a proinflammatory and hypercoagulable state, hyperglycemia and underlying comorbidities (hypertension, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease and obesity). On the other hand, a severe COVID-19 infection, and its treatment with steroids, can have a specific negative impact on diabetes itself, leading to worsening of hyperglycemia through increased insulin resistance and reduced β-cell secretory function. Worsening hyperglycemia can, in turn, adversely affect the course of COVID-19. Although more knowledge gradually surfaces as the pandemic progresses, challenges in understanding the interrelationship between COVID-19 and diabetes remain.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; comorbidities; coronavirus; diabetes; mortality; severity; treatment.
Copyright © 2021 Landstra and de Koning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, et al. . Global and Regional Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2019 and Projections for 2030 and 2045: Results From the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(Th) Edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract (2019) 157:107843. 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

