Characterization and Genomic Analysis of BUCT549, a Novel Bacteriophage Infecting Vibrio alginolyticus With Flagella as Receptor
- PMID: 34220752
- PMCID: PMC8245777
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.668319
Characterization and Genomic Analysis of BUCT549, a Novel Bacteriophage Infecting Vibrio alginolyticus With Flagella as Receptor
Abstract
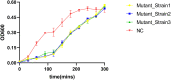
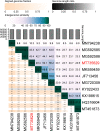
Vibrio alginolyticus is one of the most important of pathogens that can infect humans and a variety of aquatic animals, and it can cause food poisoning and septicemia in humans. Widely used antibiotics are gradually losing their usefulness, and phages are gaining more attention as new antibacterial strategies. To have more potential strategies for controlling pathogenic bacteria, we isolated a novel V. alginolyticus phage BUCT549 from seafood market sewage. It was classified as a new member of the family Siphoviridae by transmission electron microscopy and a phylogenetic tree. We propose creating a new genus for BUCT549 based on the intergenomic similarities (maximum is 56%) obtained from VIRIDIC calculations. Phage BUCT549 could be used for phage therapy due to its stability in a wide pH (3.0-11.0) range and high-temperature (up to 60°C) environment. It had a latent period of 30-40 min and a burst size of 141 PFU/infected bacterium. In the phylogenetic tree based on a terminase large subunit, BUCT549 was closely related to eight Vibrio phages with different species of host. Meanwhile, our experiments proved that BUCT549 has the ability to infect a strain of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. A coevolution experiment determined that three strains of tolerant V. alginolyticus evaded phage infestation by mutating the MSHA-related membrane protein expression genes, which caused the loss of flagellum. This research on novel phage identification and the mechanism of infestation will help phages to become an integral part of the strategy for biological control agents.
Keywords: MSHA protein; bacteriophage; genome analysis; receptor; vibrio alginolyticus.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Tian, Hu, Lin, Liu, Zhao, Ren, Pan, Shi and Tong.
Conflict of interest statement
FZ, HR, and QP are from Qingdao Phagepharm Bio-tech Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

