Pembrolizumab-Induced Thyroiditis Shows PD-L1Expressing Histiocytes and Infiltrating T Cells in Thyroid Tissue - A Case Report
- PMID: 34220792
- PMCID: PMC8250423
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.606056
Pembrolizumab-Induced Thyroiditis Shows PD-L1Expressing Histiocytes and Infiltrating T Cells in Thyroid Tissue - A Case Report
Abstract
Context: Immune-related adverse events frequently take place after initiation of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) therapy. The thyroid gland is the endocrine organ most commonly affected by ICI therapy, the pathological mechanism is still poorly understood.
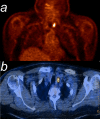
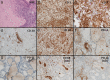
Case description: A 60-year old Upper Austrian male melanoma patient under pembrolizumab therapy received thyroidectomy because of a suspicious FDG avid thyroid nodule. Histopathology showed a pattern comparable with thyroiditis de Quervain. The inflammatory process consisted predominantly of T lymphocytes with a dominance of CD4+ T helper cells. In addition CD68+ histiocytes co-expressing PD-L1 were observed.
Conclusion: Clusters of perifollicular histiocytes expressing PD-L1 were observed in this case of pembrolizumab induced thyroiditis - probably induced by the former ICI therapy. This finding might indicate the initial target for the breakdown of self tolerance. In context with other data the immunological process seems to be driven by CD3+ lymphocytes infiltrating the thyroid.
Keywords: FDG; PET; melanoma; pembrolizumab; thyroiditis.
Copyright © 2021 Jabkowski, Loidl, Auinger, Kehrer, Sepp and Pichler.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

