A Tale of Two Immune Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Crosstalk Between Macrophages and T Cells in the Synovium
- PMID: 34220809
- PMCID: PMC8248486
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.655477
A Tale of Two Immune Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Crosstalk Between Macrophages and T Cells in the Synovium
Abstract
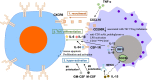
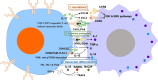
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease. Joint inflammation of RA is closely related to infiltration of immune cells, synovium hyperplasia, and superfluous secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, which lead to cartilage degradation and bone erosion. The joint synovium of RA patients contains a variety of immune cellular types, among which monocytes/macrophages and T cells are two essential cellular components. Monocytes/macrophages can recruit and promote the differentiation of T cells into inflammatory phenotypes in RA synovium. Similarly, different subtypes of T cells can recruit monocytes/macrophages and promote osteoblast differentiation and production of inflammatory cytokines. In this review, we will discuss how T cell-monocyte/macrophage interactions promote the development of RA, which will provide new perspectives on RA pathogenesis and the development of targeted therapy.
Keywords: RA; T cells; macrophage; pathogenesis; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2021 Tu, Huang, Zhang, Mei and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Giannini D, Antonucci M, Petrelli F, Bilia S, Alunno A, Puxeddu I. One Year in Review 2020: Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol (2020) 38:387–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

