Glycophosphopeptical AM3 Food Supplement: A Potential Adjuvant in the Treatment and Vaccination of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 34220861
- PMCID: PMC8248499
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.698672
Glycophosphopeptical AM3 Food Supplement: A Potential Adjuvant in the Treatment and Vaccination of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
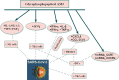
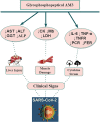
The world is currently experiencing the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-2 (SARS-CoV-2). Its global spread has resulted in millions of confirmed infections and deaths. While the global pandemic continues to grow, the availability of drugs to treat COVID-19 infections remains limited to supportive treatments. Moreover, the current speed of vaccination campaigns in many countries has been slow. Natural substrates with biological immunomodulatory activity, such as glucans, may represent an adjuvant therapeutic agent to treat SARS-CoV-2. AM3, a natural glycophosphopeptical, has previously been shown to effectively slow, with no side effects, the progression of infectious respiratory diseases by regulating effects on innate and adaptive immunity in experimental models. No clinical studies, however, exist on the use of AM3 in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. This review aims to summarize the beneficial effects of AM3 on respiratory diseases, the inflammatory response, modulation of immune response, and attenuation of muscle. It will also discuss its potential effects as an immune system adjuvant for the treatment of COVID-19 infections and adjuvant for SARS-CoV-2 vaccination.
Keywords: AM3; COVID-19; cytokines; food supplement; glycophosphopeptical; immunonutrition; muscular damage; vaccination.
Copyright © 2021 Fernández-Lázaro, Fernandez-Lazaro, Mielgo-Ayuso, Adams, García Hernández, González-Bernal and González-Gross.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) . Questions and Answers About the COVID-19 Transmission. (2021). [cited 2021 May 19] Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/coronavirus-disease-covid-19-ho....
-
- Covid-19 Map - Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center (2021). [cited 2021 May 25] Available at: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
-
- Fernández-Lázaro D, Gómez NS, Serrano NS, Sosse AA, Aldea-Mansilla C. Emergency Standardization for SARS-CoV-2 Virus Diagnosis by Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (Rt-PCR) in COVID-19 Pandemic Situation. REMASP (2020) 4:1–11. 10.36300/remasp.2020.070 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

