Potential Networks of Nitrogen-Phosphorus-Potassium Channels and Transporters in Arabidopsis Roots at a Single Cell Resolution
- PMID: 34220911
- PMCID: PMC8242960
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.689545
Potential Networks of Nitrogen-Phosphorus-Potassium Channels and Transporters in Arabidopsis Roots at a Single Cell Resolution
Abstract
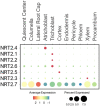
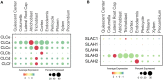
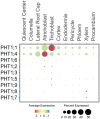
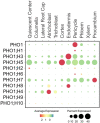
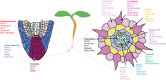
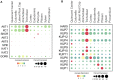
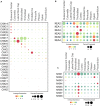
Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are three major macronutrients essential for plant life. These nutrients are acquired and transported by several large families of transporters expressed in plant roots. However, it remains largely unknown how these transporters are distributed in different cell-types that work together to transfer the nutrients from the soil to different layers of root cells and eventually reach vasculature for massive flow. Using the single cell transcriptomics data from Arabidopsis roots, we profiled the transcriptional patterns of putative nutrient transporters in different root cell-types. Such analyses identified a number of uncharacterized NPK transporters expressed in the root epidermis to mediate NPK uptake and distribution to the adjacent cells. Some transport genes showed cortex- and endodermis-specific expression to direct the nutrient flow toward the vasculature. For long-distance transport, a variety of transporters were shown to express and potentially function in the xylem and phloem. In the context of subcellular distribution of mineral nutrients, the NPK transporters at subcellular compartments were often found to show ubiquitous expression patterns, which suggests function in house-keeping processes. Overall, these single cell transcriptomic analyses provide working models of nutrient transport from the epidermis across the cortex to the vasculature, which can be further tested experimentally in the future.
Keywords: NPK transport networks; expression analysis; nitrate transport; nutrient transporters; phosphate transport; potassium transport; root single cell transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2021 Lhamo and Luan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Getting to the roots of N, P, and K uptake.J Exp Bot. 2023 Mar 28;74(6):1784-1805. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erad035. J Exp Bot. 2023. PMID: 36708176 Review.
-
The endodermis as a checkpoint for nutrients.New Phytol. 2017 Mar;213(4):1604-1610. doi: 10.1111/nph.14140. Epub 2016 Aug 23. New Phytol. 2017. PMID: 27551946 Review.
-
Nitrate-induced genes in tomato roots. Array analysis reveals novel genes that may play a role in nitrogen nutrition.Plant Physiol. 2001 Sep;127(1):345-59. doi: 10.1104/pp.127.1.345. Plant Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11553762 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue and nitrogen-linked expression profiles of ammonium and nitrate transporters in maize.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 May 20;19(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1768-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31109290 Free PMC article.
-
Plant tissue analysis as a tool for predicting fertiliser needs for low cyanogenic glucoside levels in cassava roots: An assessment of its possible use.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 13;15(2):e0228641. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228641. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32053630 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nitrogen sensing and regulatory networks: it's about time and space.Plant Cell. 2024 May 1;36(5):1482-1503. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae038. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 38366121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Back From the Dead: The Atypical Kinase Activity of a Pseudokinase Regulator of Cation Fluxes During Inducible Immunity.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 11;13:931324. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.931324. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36035673 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities and challenges in the application of single-cell and spatial transcriptomics in plants.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Aug 11;14:1185377. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1185377. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37636094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Five Post-Translational Modification Residues of CmPT2 Play Key Roles in Yeast and Rice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 19;24(3):2025. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032025. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768347 Free PMC article.
-
Utilizing machine learning to optimize agricultural inputs for improved rice production benefits.iScience. 2024 Nov 16;27(12):111407. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111407. eCollection 2024 Dec 20. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39687017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An R., Chen Q.-J., Chai M.-F., Lu P.-L., Su Z., Qin Z.-X., et al. (2007). AtNHX8, a member of the monovalent cation: proton antiporter-1 family in Arabidopsis thaliana, encodes a putative Li/H antiporter: AtNHX8 encodes an Li+/H+ antiporter. Plant J. 49 718–728. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02990.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

