Mastoid obliteration and reconstruction techniques: A review of the literature
- PMID: 34220986
- PMCID: PMC8241697
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joto.2021.01.002
Mastoid obliteration and reconstruction techniques: A review of the literature
Abstract
Objective: To review the published literature related to the different obliteration and reconstruction techniques in the management of the canal wall down mastoidectomy.
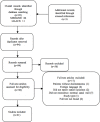
Methods: A PubMed (Medline) and LILACS databases as well as crossed references search was performed with the following Mesh terms: "cholesteatoma", "cholesteatoma-middle ear", "otitis media", "otitis media, suppurative", "mastoiditis", "mastoidectomy", "canal wall down mastoidectomy", "radical mastoidectomy", "mastoid obliteration" and crossed references. Inclusion criteria were adult patients subject to mastoid cavity obliteration and posterior canal wall reconstruction. The technique and materials used, anatomic and functional results, complications, recurrence rates, and changes in quality of life, were analyzed. A total of 94 articles were screened, 38 were included for full-text detailed review.
Results: Twenty-one articles fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Techniques and materials used for canal wall reconstruction, tympanoplasty, and ossiculoplasty were varied and included autologous, biosynthetic, or both. Auditory results were reported in 16 studies and were inconsistent. Three studies reported improvement in the quality of life using the GBI scale. Follow-up time ranged from 1 to 83 months. Eleven articles used imaging studies to evaluate postoperative disease recurrence. The highest recurrence rate reported for cholesteatoma after obliteration was 19%. The most frequently reported complications were retraction pockets and transient otorrhea.
Conclusion: Plenty of techniques combining grafts and other materials have been used to overcome mastoidectomy cavity problems. So far, it is still not possible to standardize an ideal procedure. The available level of evidence for this topic is low and limited.
Keywords: Cholesteatoma; Chronic otitis media; Mastoid obliteration; Mastoidectomy; Quality of life.
© 2021 PLA General Hospital Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. Production and hosting by Elsevier (Singapore) Pte Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A technique for concurrent procedure of mastoid obliteration and meatoplasty after canal wall down mastoidectomy.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2012 Dec;39(6):557-61. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2011.11.004. Epub 2012 Feb 8. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2012. PMID: 22321811
-
Mastoid Obliteration with Autologous Bone in Mastoidectomy Canal Wall Down Surgery: a Literature Overview.Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Jan;20(1):76-83. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1563382. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26722350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mastoid Obliteration Using Autologous Bone Dust Following Canal Wall Down Mastoidectomy.Otol Neurotol. 2021 Jan;42(1):68-75. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002839. Otol Neurotol. 2021. PMID: 32976343
-
Mastoid Obliteration with Synthetic Materials: A Review of the Literature.J Int Adv Otol. 2019 Dec;15(3):400-404. doi: 10.5152/iao.2019.7038. J Int Adv Otol. 2019. PMID: 31846919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outcomes of Modified Canal Wall Down Mastoidectomy and Mastoid Obliteration Using Autologous Materials.Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Nov;12(4):360-366. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2018.01333. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 30700087 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Post-auricular Soft Tissue and Post-auricular Soft Tissue With Autologous Bone Pate in Obliteration of the Canal Wall Down Mastoidectomy Cavity.Cureus. 2024 Dec 15;16(12):e75734. doi: 10.7759/cureus.75734. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39811213 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrence in cholesteatoma surgery: what have we learnt and where are we going? A narrative review.Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2023 Apr;43(Suppl 1):S48-S55. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-suppl.1-43-2023-06. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2023. PMID: 37698100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mastoid Obliteration Using S53P4 Bioactive Glass Versus Mastoidectomy Alone for Refractory Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media.Otol Neurotol. 2025 Sep 1;46(8):949-955. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000004545. Otol Neurotol. 2025. PMID: 40788269 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective Analysis of Postoperative Effect of Supratubal Recess Opened and Bony Obliteration Tympanoplasty.J Int Adv Otol. 2023 Mar;19(2):105-111. doi: 10.5152/iao.2023.22758. J Int Adv Otol. 2023. PMID: 36975082 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of S53P4 Bioactive Glass for the Secondary Obliteration of Chronically Discharging Radical Cavities.OTO Open. 2023 Nov 29;7(4):e96. doi: 10.1002/oto2.96. eCollection 2023 Oct-Dec. OTO Open. 2023. PMID: 38034064 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources