Simultaneous Proximal Median and Ulnar Neuropathy: A Rare Complication of 24-hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring with Unexpected Neurophysiological Findings
- PMID: 34221168
- PMCID: PMC8224729
- DOI: 10.26574/maedica.2020.16.1.130
Simultaneous Proximal Median and Ulnar Neuropathy: A Rare Complication of 24-hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring with Unexpected Neurophysiological Findings
Abstract
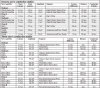
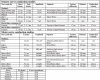
Introduction:Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) is a non-invasive method of obtaining brachial artery pressure assessment over 24 hours while patients undergo normal daily activities. Side effects, such as peripheral petechiae, limb edema, and sleep disturbance, are usually mild and reversible. Case report:A 67-year-old male presented with excruciating left hand pain and weakness on waking up from night sleep, having worn a cuff on his left arm for a whole day in the context of 24-hour ABPM. Clinical extremeexamination confirmed hypoesthesia in the left median and ulnar nerve distribution and weakness solely affecting ulnar and sparing median innervated hand muscles. Neurophysiological testing was performed. Interestingly, although median and ulnar motor responses were abnormal the respective sensory responses were unremarkable. Conclusion:To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of simultaneous proximal median and ulnar neuropathy complicating 24-hour ABPM. From a neurophysiological standpoint, it is also intriguing as this is a rare case of peripheral neuropathy with prominent motor fibre involvement, but normal sensory responses.
Figures
References
-
- Beltman FW, Heesen WF, Smit AJ, et al. Acceptance and side effects of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: evaluation of a new technology. J Hum Hypertens. 1996;10 Suppl 3:S39–S42. - PubMed
-
- Tapolyai M, Udvari-Nagy S, Schede-Don K. The rate of complications of 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) is low. Am J Hypertens. 2001;14(5 Pt 1):487–488. - PubMed
-
- Pudich J, Plášek J, Homza M. Type II complex regional pain syndrome resulting in a persistent contracture of the left hand: A severe side effect of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Coretvasa 59.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources