Outcomes of brain metastasis in high-grade bone and soft tissue sarcoma: An analysis of clinicopathological characteristics and survival data
- PMID: 34221290
- PMCID: PMC8221671
- DOI: 10.1177/20363613211026151
Outcomes of brain metastasis in high-grade bone and soft tissue sarcoma: An analysis of clinicopathological characteristics and survival data
Abstract
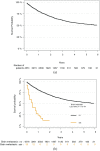
Brain metastases in sarcoma are exceedingly rare, with few published series documenting ranges from 1% to 8%. This study investigated the outcomes of sarcoma patients with brain metastases using a population-based analysis. This was a retrospective review of 5933 patients with high-grade sarcoma identified from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database between 2010 and 2015. Of the eligible 5933 patients, 0.7% (n = 44) had brain metastasis. Kaplan-Meier was used to estimate survival and follow-up (reverse Kaplan-Meier), and a multivariable Cox proportional hazards model analyzed prognostic factors of disease-free survival (DFS). Median (IQR) follow-up of all eligible patients was 28 months (12; 47). Patients who developed brain metastasis had a higher proportion of N1 stage disease (p < 0.001), as well as synchronous metastasis to bones, liver, and lungs compared to those without brain metastasis (all p < 0.001). The median (IQR) DFS with brain metastasis was 6 months (2; 12), and survival with brain metastasis was significantly worse than DFS in patients without brain metastasis (p < 0.001). Among those with brain metastasis only, there was no difference in DFS with respect to sex, race, primary tumor origin, T stage or N stage disease, synchronous metastasis to bone, liver or lung, nor with respect to chemotherapy or radiation for treatment of the primary tumor (all p > 0.05). For sarcoma patients with brain metastasis, the outcomes are poor and do not appear to differ by clinicopathologic factors. However, patients with certain histologies and synchronous metastases may warrant more frequent surveillance as there was an association of brain metastasis with these factors.
Keywords: Sarcoma; brain metastases; outcomes; prognosis; survival.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interest: The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Alan Blank is an ad hoc reviewer/editorial governing board for the journal of Rare Tumors.
Figures
References
-
- Norden AD, Wen PY, Kesari S. Brain metastases. Curr Opin Neurol 2005; 18(6): 654–661. - PubMed
-
- Bindal RK, Sawaya RE, Leavens ME, et al.. Sarcoma metastatic to the brain: results of surgical treatment. Neurosurgery 1994; 35(2): 185–190. - PubMed
-
- Espat NJ, Bilsky M, Lewis JJ, et al.. Soft tissue sarcoma brain metastases. Prevalence in a cohort of 3829 patients. Cancer 2002; 94(10): 2706–2711. - PubMed
-
- Wroński M, Arbit E, Burt M, et al.. Resection of brain metastases from sarcoma. Ann Surg Oncol 1995; 2(5): 392–399. - PubMed
-
- Fox BD, Patel A, Suki D, et al.. Surgical management of metastatic sarcoma to the brain. J Neurosurg 2009; 110: 181–186. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

