Prediction of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on nutrition data
- PMID: 34221364
- PMCID: PMC8223171
- DOI: 10.1017/jns.2021.36
Prediction of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on nutrition data
Abstract
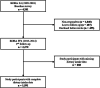
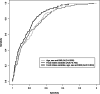
Numerous predictive models for the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) exist, but a minority of them has implemented nutrition data so far, even though the significant effect of nutrition on the pathogenesis, prevention and management of T2DM has been established. Thus, in the present study, we aimed to build a predictive model for the risk of T2DM that incorporates nutrition data and calculates its predictive performance. We analysed cross-sectional data from 1591 individuals from the population-based Cooperative Health Research in the Region of Augsburg (KORA) FF4 study (2013-14) and used a bootstrap enhanced elastic net penalised multivariate regression method in order to build our predictive model and select among 193 food intake variables. After selecting the significant predictor variables, we built a logistic regression model with these variables as predictors and T2DM status as the outcome. The values of area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV) and accuracy of our predictive model were calculated. Eleven out of the 193 food intake variables were selected for inclusion in our model, which yielded a value of area under the ROC curve of 0⋅79 and a maximum PPV, NPV and accuracy of 0⋅37, 0⋅98 and 0⋅91, respectively. The present results suggest that nutrition data should be implemented in predictive models to predict the risk of T2DM, since they improve their performance and they are easy to assess.
Keywords: 24HFL, 24-h food list; Elastic net regression; KORA, Cooperative Health Research in the Region of Augsburg; NPV, negative predictive value; Nutrition; PPV, positive predictive value; Prediction model; ROC, receiver operating characteristic; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; Type 2 diabetes.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Learning from the machine: is diabetes in adults predicted by lifestyle variables? A retrospective predictive modelling study of NHANES 2007-2018.BMJ Open. 2025 Mar 22;15(3):e096595. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-096595. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40122552 Free PMC article.
-
Differential associations between diet and prediabetes or diabetes in the KORA FF4 study.J Nutr Sci. 2018 Dec 27;7:e34. doi: 10.1017/jns.2018.25. eCollection 2018. J Nutr Sci. 2018. PMID: 30627431 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus using artificial neural network: an effective classification approach.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013 Apr;100(1):111-8. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2013.01.023. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013. PMID: 23453177
-
Comparison of traditional diabetes risk scores and HbA1c to predict type 2 diabetes mellitus in a population based cohort study.J Diabetes Complications. 2017 Nov;31(11):1602-1607. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2017.07.016. Epub 2017 Aug 1. J Diabetes Complications. 2017. PMID: 28886990
-
Implementation status of prediction models for type 2 diabetes.Prim Care Diabetes. 2023 Dec;17(6):655-657. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2023.09.002. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Prim Care Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37735030 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of a nomogram of all-cause mortality in adult Americans with diabetes.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 19;14(1):19148. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69581-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39160223 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-based self-diagnosis tool for diabetes.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Nov;10(21):1158. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-2195. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36467364 Free PMC article.
-
Implementing a Novel Machine Learning System for Nutrition Education in Diabetes Mellitus Nutritional Clinic: Predicting 1-Year Blood Glucose Control.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Sep 28;10(10):1139. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10101139. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37892869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, et al. (2019) Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 157, 107843. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

