Pro-calcifying analysis of uraemic serum from patients treated with medium cut-off membrane in a prospective, cross-over study
- PMID: 34221387
- PMCID: PMC8243281
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa216
Pro-calcifying analysis of uraemic serum from patients treated with medium cut-off membrane in a prospective, cross-over study
Abstract
Background: The retention of a large number of solutes that are normally excreted or metabolized by the kidney is responsible for the symptoms typical in uraemic patients. These molecules are defined as uraemic toxins and can be classified into three groups: small water-soluble molecules, middle molecules and protein-bound toxins. Recently, efforts were put towards developing dialysis membranes that allow the removal of large middle molecules without clinically relevant albumin loss. These membranes are the medium cut-off (MCO) membranes that allow the removal of middle molecules up to ∼50 000 Da.
Methods: We performed a prospective, open-label, controlled, cross-over pilot study comparing expanded haemodialysis (HDx) (novel MCO membrane Theranova 400) and conventional haemodialysis (HD) in 20 prevalent HD patients. Ten patients used conventional HD high-flux dialyser and 10 patients used HDx for 3 months; later the patients switched and received the other treatment for a further 3 months. We then analysed the pro-calcifying effect of uraemic serum in a model of high phosphate(Pi)-induced calcification in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs).
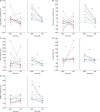
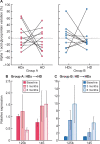
Results: In this study, every patient was the control of himself and, interestingly, we found a tendency of less pro-calcifying potential from HDx-treated patients' serum compared with HD. Studying pathogenetic processes involved in high Pi-induced calcium deposition, we found that uraemic serum of HDx-treated patients induced less VSMC necrosis compared with uraemic serum of HD patients. Nevertheless, no differences were found between the different dialytic treatments in the serum potential to induce apoptosis and to modulate the expression of a panel of genes involved in VSMC simil-osteoblastic differentiation such as bone morphogenetic protein 2, runt-related transcription factor 2, osteocalcin, matrix Gla protein, osteopontin, elastin and collagen I α1. In an effort to characterize the difference in uraemic toxin profile during the two different dialytic treatments, we measured a panel of 10 uraemic toxins and 3 precursors, finding a significant increased removal during HDx of 3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2-furanpropanoic acid, tryptophane and some of its metabolites, such as 3-indoxyl sulphate, indole 3-acetic acid and kynurenine.
Conclusions: These preliminary data are promising, although larger patients' groups are needed to better understand the effects of HDx on vascular calcification.
Keywords: necrosis; protein-bound uraemic toxins; uraemic serum; vascular calcification.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of a medium cut-off (Theranova®) dialyser on haemodialysis patients: a prospective, cross-over study.Clin Kidney J. 2019 Nov 11;14(1):382-389. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfz155. eCollection 2021 Jan. Clin Kidney J. 2019. PMID: 33564442 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the super-flux cellulose triacetate dialyser membrane on the removal of non-protein-bound and protein-bound uraemic solutes.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007 Jul;22(7):2006-12. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm065. Epub 2007 Apr 27. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007. PMID: 17468506
-
Removal of large middle molecules via haemodialysis with medium cut-off membranes at lower blood flow rates: an observational prospective study.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Dec 31;21(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1669-3. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31892319 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The membrane perspective of uraemic toxins: which ones should, or can, be removed?Clin Kidney J. 2021 Dec 27;14(Suppl 4):i17-i31. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfab202. eCollection 2021 Dec. Clin Kidney J. 2021. PMID: 34987783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Removal of protein-bound uraemic toxins by haemodialysis.Blood Purif. 2013;35 Suppl 2:20-5. doi: 10.1159/000350843. Epub 2013 May 3. Blood Purif. 2013. PMID: 23676831 Review.
Cited by
-
Trial design of the MOTheR HDx study: a multicenter, open-label, prospective, randomized study to explore the morbidity and mortality in patients dialyzed with the Theranova HDx in comparison with online hemodiafiltration.Clin Kidney J. 2023 May 27;16(11):2254-2261. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad128. eCollection 2023 Nov. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 37915938 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Medium Cut-Off Versus High-Flux Hemodialysis Membranes on Biomarkers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2022 Jan 18;9:20543581211067090. doi: 10.1177/20543581211067090. eCollection 2022. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2022. PMID: 35070336 Free PMC article.
-
Kynurenine Promotes Phosphate-Induced Endothelial Calcification via Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition, Osteoblastic Differentiation and AhR Activation.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Aug 19;17(8):421. doi: 10.3390/toxins17080421. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40864097 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the kynurenine pathway in cardiovascular disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 May 31;11:1406856. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1406856. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38883986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expanded Haemodialysis as a Current Strategy to Remove Uremic Toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2021 May 26;13(6):380. doi: 10.3390/toxins13060380. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34073439 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Covic A, Vervloet M, Massy ZA. et al. Bone and mineral disorders in chronic kidney disease: implications for cardiovascular health and ageing in the general population. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2018; 6: 319–331 - PubMed
-
- Ciceri P, Galassi A, Alfieri C. et al. Uremic patients with increased vascular calcification score have serum with high calcific potential: role of vascular smooth muscle cell osteoblastic differentiation and apoptosis. Blood Purif 2019; 48: 142–149 - PubMed
-
- Ciceri P, Volpi E, Brenna I. et al. Combined effects of ascorbic acid and phosphate on rat VSMC osteoblastic differentiation. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2012; 27: 122–127 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

