Bactericidal fully human single-chain fragment variable antibodies protect mice against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia
- PMID: 34221401
- PMCID: PMC8240403
- DOI: 10.1002/cti2.1302
Bactericidal fully human single-chain fragment variable antibodies protect mice against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia
Abstract
Objectives: The increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, besides the inadequate numbers of effective antibiotics, emphasises the need to find new therapeutic agents against this lethal pathogen.
Methods: In this study, to obtain antibody fragments against S. aureus, a human single-chain fragment variable (scFv) library was enriched against living methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) cells, grown in three different conditions, that is human peripheral blood mononuclear cells with plasma, whole blood and biofilm. The antibacterial activity of scFvs was evaluated by the growth inhibition assay in vitro. Furthermore, the therapeutic efficacy of anti-S. aureus scFvs was appraised in a mouse model of bacteraemia.
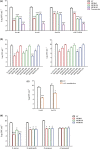
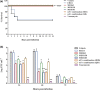
Results: Three scFv antibodies, that is MEH63, MEH158 and MEH183, with unique sequences, were found, which exhibited significant binding to S. aureus and reduced the viability of S. aureus in in vitro inhibition assays. Based on the results, MEH63, MEH158 and MEH183, in addition to their combination, could prolong the survival rate, reduce the bacterial burden in the blood and prevent inflammation and tissue destruction in the kidneys and spleen of mice with MRSA bacteraemia compared with the vehicle group (treated with normal saline).
Conclusion: The combination therapy with anti-S. aureus scFvs and conventional antibiotics might shed light on the treatment of patients with S. aureus infections.
Keywords: bacteraemia; bactericidal antibodies; fully human antibody; methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcusaureus; single‐chain fragment variable.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical & Translational Immunology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Australian and New Zealand Society for Immunology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Lowy FD. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med 1998; 339: 520–532. - PubMed
-
- Lehar SM, Pillow T, Xu M et al. Novel antibody–antibiotic conjugate eliminates intracellular S. aureus . Nature 2015; 527: 323–328. - PubMed
-
- Lee AS, de Lencastre H , Garau J et al. Methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus . Nat Rev Dis 2018; 4: 1–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
