Neuromodulation in Drug Resistant Epilepsy
- PMID: 34221550
- PMCID: PMC8219496
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2021.0211
Neuromodulation in Drug Resistant Epilepsy
Abstract
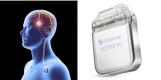
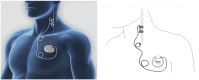
Epilepsy affects approximately 70 million people worldwide, and it is a significant contributor to the global burden of neurological disorders. Despite the advent of new AEDs, drug resistant-epilepsy continues to affect 30-40% of PWE. Once identified as having drug-resistant epilepsy, these patients should be referred to a comprehensive epilepsy center for evaluation to establish if they are candidates for potential curative surgeries. Unfortunately, a large proportion of patients with drug-resistant epilepsy are poor surgical candidates due to a seizure focus located in eloquent cortex, multifocal epilepsy or inability to identify the zone of ictal onset. An alternative treatment modality for these patients is neuromodulation. Here we present the evidence, indications and safety considerations for the neuromodulation therapies in vagal nerve stimulation (VNS), responsive neurostimulation (RNS), or deep brain stimulation (DBS).
Keywords: DBS; RNS; VNS; drug-resistant epilepsy; epilepsy; neuromodulation; neurostimulation.
copyright: © 2021 Rincon et al.
Figures

References
-
- Kanner AM (2016). Management of psychiatric and neurological comorbidities in epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol, 12:106-116. - PubMed
-
- Gilliam F, Kuzniecky R, Faught E, Black L, Carpenter G, Schrodt R (1997). Patient-validated content of epilepsy-specific quality-of-life measurement. Epilepsia, 38:233-236. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
