Mid-Regional Proadrenomedullin and Mid-Regional Proatrial Natriuretic Peptide Clearance Predicts Poor Outcomes Better Than Single Baseline Measurements in Critically Ill Patients With Pneumonia: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 34221750
- PMCID: PMC8237920
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.15285
Mid-Regional Proadrenomedullin and Mid-Regional Proatrial Natriuretic Peptide Clearance Predicts Poor Outcomes Better Than Single Baseline Measurements in Critically Ill Patients With Pneumonia: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
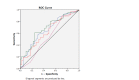
Background We assessed the ability of baseline and serial measurements of mid-regional proadrenomedullin (MR-proADM) and mid-regional proatrial natriuretic peptide (MR-proANP) to predict 28-day mortality in critically ill patients with pneumonia compared with Acute Physiological and Chronic Health Evaluation IV (APACHE IV) model and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score. Methodology Biomarkers were collected for the first five days in this retrospective observational cohort study. Biomarker clearance (as a percentage) was presented as biomarker decline in five days. We investigated the relationship between biomarkers and mortality in a multivariable Cox regression model. APACHE IV and SOFA were calculated after 24 hours from intensive care unit admission. Results In 153 critically ill patients with pneumonia, 28-day mortality was 26.8%. Values of baseline MR-proADM, MR-proANP, and APACHE IV were significantly higher in 28-day nonsurvivors, but not significantly different for SOFA score. Baseline MR-proADM and MR-proANP, APACHE IV, and SOFA had a low area under the curve in receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves. No optimal cut-off points could be calculated. Biomarkers and severity scores were divided into tertiles. The highest tertiles baseline MR-proADM and MR-proANP were not significant predictors for 28-day mortality in a multivariable model with age and APACHE IV. SOFA was not a significant predictor in univariable analysis. Clearances of MR-proADM and MR-proANP were significantly higher in 28-day survivors. MR-proADM and MR-proANP clearances had similar low accuracy to identify nonsurvivors in ROC curves and were divided into tertiles. Low clearances of MR-proADM and MR-proANP (first tertiles) were significant predictors for 28-day mortality (hazard ratio [HR]: 2.38; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.21-4.70; p = 0.013 and HR: 2.27; 95% CI: 1.16-4.46; p = 0.017) in a model with age and APACHE IV. Conclusions MR-proADM and MR-proANP clearance performed better in predicting 28-day mortality in a model with age and APACHE IV compared with single baseline measurements in a mixed population of critically ill with pneumonia.
Keywords: apache iv; biomarkers; mr-proadm; mr-proanp; pneumonia; sofa.
Copyright © 2021, Van Oers et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endothelium-associated biomarkers mid-regional proadrenomedullin and C-terminal proendothelin-1 have good ability to predict 28-day mortality in critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: A prospective cohort study.J Crit Care. 2021 Dec;66:173-180. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2021.07.017. Epub 2021 Jul 20. J Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 34340901 Free PMC article.
-
High levels of mid-regional proadrenomedullin in ARDS COVID-19 patients: the experience of a single, Italian Center.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Feb;25(3):1743-1751. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202102_24885. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33629344
-
Superior accuracy of mid-regional proadrenomedullin for mortality prediction in sepsis with varying levels of illness severity.Ann Intensive Care. 2017 Dec;7(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13613-017-0238-9. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Ann Intensive Care. 2017. PMID: 28185230 Free PMC article.
-
Proadrenomedullin in the Management of COVID-19 Critically Ill Patients in Intensive Care Unit: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Evidence and Uncertainties in Existing Literature.J Clin Med. 2022 Aug 4;11(15):4543. doi: 10.3390/jcm11154543. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35956159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MR-proANP levels in Acute ischemic stroke and clinical outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Rev. 2024 Nov 5;47(1):835. doi: 10.1007/s10143-024-03073-w. Neurosurg Rev. 2024. PMID: 39496843
Cited by
-
Mid-regional proadrenomedullin, C-terminal proendothelin-1 values, and disease course are not different in critically ill SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia patients with obesity.Int J Obes (Lond). 2022 Oct;46(10):1801-1807. doi: 10.1038/s41366-022-01184-2. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Int J Obes (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35840771 Free PMC article.
-
Mid-Regional Proadrenomedullin (MR-proADM) and Microcirculation in Monitoring Organ Dysfunction of Critical Care Patients With Infection: A Prospective Observational Pilot Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 30;8:680244. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.680244. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34917627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clinical practice. Community-acquired pneumonia. Wunderink RG, Waterer GW. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:543–551. - PubMed
-
- Community-acquired pneumonia. Musher DM, Thorner AR. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1619–1628. - PubMed
-
- Mortality in ICU patients with bacterial community-acquired pneumonia: when antibiotics are not enough. Rodriguez A, Lisboa T, Blot S, Martin-Loeches I, Solé-Violan J, De Mendoza D, Rello J. Intensive Care Med. 2009;35:430–438. - PubMed
-
- Guidelines for the management of adults with hospital-acquired, ventilator-associated, and healthcare-associated pneumonia. American Thoracic Society, Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171:388–416. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
