Development and Longitudinal Analysis of Plan-Based Streamlined Quality Assurance on Multiple Positioning Guidance Systems With Single Phantom Setup
- PMID: 34222005
- PMCID: PMC8242243
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.683733
Development and Longitudinal Analysis of Plan-Based Streamlined Quality Assurance on Multiple Positioning Guidance Systems With Single Phantom Setup
Abstract
Purpose: This study was to propose and validate an efficient and streamlined quality assurance (QA) method with a single phantom setup to check performances of patient positioning guidance systems including six-degree-of-freedom (6DoF) couch, X-ray modalities (kV-kV, MV-MV and CBCT), optical surface imaging system (AlignRT), lasers and optical distance indicator (ODI).
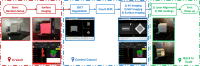
Methods and materials: The QA method was based on a pseudo-patient treatment plan using the AlignRT cube phantom. The cube was first randomly set up on the couch, and the initial position offsets were acquired by AlignRT and CBCT. The cube was restored to its reference position by 6DoF couch shift, during which the couch motion accuracy and tracking performances of AlignRT and CBCT were derived. After that, the residual offsets were acquired by kV-kV, MV-MV and AlignRT to derive the isocenter discrepancies. Finally, the laser alignment and ODI values were visually inspected. The QA procedure had been internally approved as a standard weekly QA test, and the results over 50 weeks were longitudinally analyzed for clinical validation.
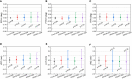
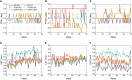
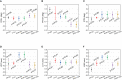
Results: The 6DoF couch motion errors as well as the tracking errors of AlignRT were sub-millimeter and sub-degree, and no deviation over 1 mm or 1 deg was identified. The ROI mode of isocenter (ISO) in AlignRT exhibited more consistent results than the centroid (CEN). While the isocenter discrepancy between CBCT and kV-kV was negligible, the maximal discrepancies between CBCT and MV-MV were 0.4 mm in LNG and 0.3 deg in PITCH. The isocenter discrepancies between CBCT and AlignRT were <0.5 mm in translation and <0.3 deg in rotation. For AlignRT, the isocenter discrepancies between the DICOM and SGRT references were about 0.6 mm in VRT, 0.5 mm in LNG and 0.2 deg in PITCH. As the therapists became familiar with the workflow, the average time to complete the whole procedure was around 23 min.
Conclusions: The streamlined QA exhibits desirable practicality as an efficient multipurpose performance check on positioning guidance systems. The stability, tracking performance and isocenter congruence of the positioning guidance systems have been fully validated for all clinical image guidance RT application, even SRS/SBRT, which requires the strictest tolerance.
Keywords: image guided radiotherapy; positioning guidance; quality assurance; robotic couch; surface imaging.
Copyright © 2021 Zhou, Li, Du, Yu, Wang, Wu and Yue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Yin FF, Wong J, Balter JM, Benedict S, Bissonnette JP, Craig T, et al. . The Role of In-Room kV X-Ray Imaging for Patient Setup and Target Localization. College Park, MD: American Association of Physicists in Medicine; (2009). 10.37206/104 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

