A Fibrinogen Alpha Fragment Mitigates Chemotherapy-Induced MLL Rearrangements
- PMID: 34222016
- PMCID: PMC8249925
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.689063
A Fibrinogen Alpha Fragment Mitigates Chemotherapy-Induced MLL Rearrangements
Abstract
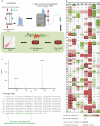
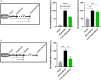
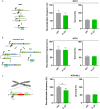
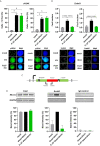
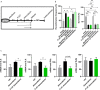
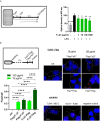
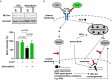
Rearrangements in the Mixed Lineage Leukemia breakpoint cluster region (MLLbcr) are frequently involved in therapy-induced leukemia, a severe side effect of anti-cancer therapies. Previous work unraveled Endonuclease G as the critical nuclease causing initial breakage in the MLLbcr in response to different types of chemotherapeutic treatment. To identify peptides protecting against therapy-induced leukemia, we screened a hemofiltrate-derived peptide library by use of an enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)-based chromosomal reporter of MLLbcr rearrangements. Chromatographic purification of one active fraction and subsequent mass spectrometry allowed to isolate a C-terminal 27-mer of fibrinogen α encompassing amino acids 603 to 629. The chemically synthesized peptide, termed Fα27, inhibited MLLbcr rearrangements in immortalized hematopoietic cells following treatment with the cytostatics etoposide or doxorubicin. We also provide evidence for protection of primary human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells from therapy-induced MLLbcr breakage. Of note, fibrinogen has been described to activate toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Dissecting the Fα27 mode-of action revealed association of the peptide with TLR4 in an antagonistic fashion affecting downstream NFκB signaling and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. In conclusion, we identified a hemofiltrate-derived peptide inhibitor of the genome destabilizing events causing secondary leukemia in patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Keywords: Endonuclease G; bioactive peptide; doxorubicin; hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells; inflammatory signaling; mixed lineage leukemia.
Copyright © 2021 Eberle, Wiehe, Gole, Mattis, Palmer, Ständker, Forssmann, Münch, Gebhardt and Wiesmüller.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- De Braekeleer M, Morel F, Le Bris MJ, Herry A, Douet-Guilbert N. The MLL Gene and Translocations Involving Chromosomal Band 11q23 in Acute Leukemia. Anticancer Res (2005) 25:1931–44. - PubMed
-
- Gleissner B, Goekbuget N, Rieder H, Arnold R, Schwartz S, Diedrich H, et al. . CD10- Pre-B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) Is a Distinct High-Risk Subgroup of Adult ALL Associated With a High Frequency of MLL Aberrations: Results of the German Multicenter Trials for Adult All (GMALL). Blood (2005) 106:4054–6. 10.1182/blood-2005-05-1866 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

